LO2A-B-C
advertisement

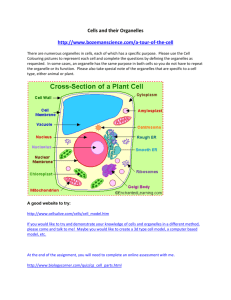
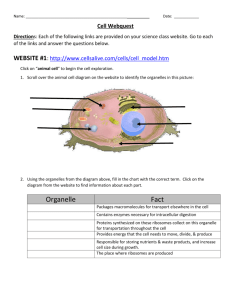
2.2: The Cell Is The Basic Unit of Life CELLS to TISSUES to ORGANS to SYSTEMS Page 103-109 Learning Outcome #2: Investigate and describe the role of cells within living things 2a) describe the role of cells as a basic unit of life 2b) analyze similarities and differences between single-celled and multicelled organisms 2c) distinguish between plant and animal cells THE CELL Use your textbook to answer the following questions. 1) The smallest unit of life is known as the __________________. An individual unit of life. 2) Cells with similar structures and functions form ____________________ and these groups work together for a common purpose form _______________ 3) Cells are the basic unit of life as they can ________________________ all the _____________________ (obtain nutrients, remove waste, and reproduce) that life depends on. (page 86) 4) Look at the size difference of the following single celled organisms and the individual plant and animal cells. 5) Each type of cell has ORGANELLES that have a job or role to do within the cell. Most cells have the same organelles. Complete the chart below based on the organelles, their functions and features to identify them. (pg. 103 & 108) LETTER FROM BELOW CELL STRUCTURE Vacuoles Mitochondria (Singular is Mitochondrion) FEATURES TO IDENTIFY IT Looks like a thin line that surrounds the whole cell A liquid inside the cell, which has grainy-like bits in it A fairly dark, spherical structure that’s usually near the center of the cell. Clear liquid filled spaces in various places within the cytoplasm FUNCTION A “controllable gateway” that lets needed materials in and waste material out The powerhouses of the cell where chemical reactions convert _____________________ to ______________________ 6) The following cell is an example of a ______________________ cell. Label the cells organelles on the cell below. (pg 109) A C D E B 7) The following diagram is of a _________________________ cell. A plant cell has two different organelles that an animal cell does not have. Label the following diagram. A F G B C D E 8) Complete the chart below about the organelles in a plant LETTER CELL STRUCTURE FEATURES TO IDENTIFY Looks like a thin line that surrounds the whole cell A rigid, frame-like covering that surrounds the cell membrane A liquid inside the cell, which has grainy-like bits in it A fairly dark, spherical structure that’s usually near the center of the cell. Vacuoles Mitochondria (Singular is Mitochondrion) Clear liquid filled spaces in various places within the cytoplasm Found in the cells of the green parts of _________________ cell. FUNCTION A “controllable gateway” that lets needed materials in and waste material out “kitchen”-contains the nutrients required to maintain its life processes. “command centre”directs all cellular activities (movement, growth, replacement) “storage rooms”nutrients, water, waste, etc. The powerhouses of the cell where chemical reactions convert energy to useable form the cell can use. 9) List two organelles found in a plant and not animal cell. 10) Explain why these two organelles are found in a plant cell and not animal cells? 11) Take a close look at the vacuoles in a plant and animal cell. Describe the difference you see. Explain why this would be a third difference between plant and animal cells. 2.3 ORGANISMS CAN BE SINGLE-CELLED OR MULTICELLED: Page 110-114 1. Unicellular means the organism is made up of ______ cell. Two examples would be _______________ and ________________. Why are unicellular organisms not classified as simple? 2. Multicellular means the organism is made up of __________ cells. Two examples are ______________________ and _________________________. How do multicellular organisms perform functions such as feeding, moving, etc.? 3. Amoebas and paramecium are examples of common __________________ organisms that live in water. They are made up of a ___________ ___________. They are able to perform all the characteristics of living things. Amoeba move using a __________________ (foot like projection) and paramecium use _________________ for locomotion.