AP Literature Review Test
advertisement

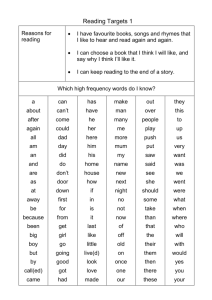
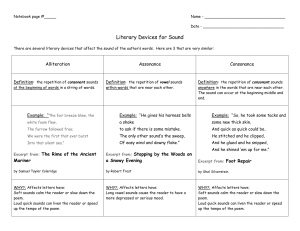
AP Literature Review Test Name_______________ Score_______ Literary Terms—DEFINITIONS Greek word for “feeling”; evokes high emotion—sorrow, pity, compassion figure of speech; author groups contradictory terms to suggest paradox giving attributes of a human being to something nonhuman statement that appears to be self-contradictory but may be true language that cannot be taken literally major category into which a literary work fits reference to art, history, literature which is presumably known reader/audience knows something a character does not implicit comparison made between two things essentially unlike a work that targets human vices (faults/follies) multiple meanings of a word, phrase, or sentence nonliteral, associative meaning of a word figure of speech; use of something closely related for the thing meant addressing someone dead or absent as if could reply representation through language of sense experience question asked not for a response but for impact/call attention to something a pleasing arrangement of sounds elaborate parallel between two seemingly dissimilar objects/ideas style of writing that combines realism with moments of fantasy brief narration of a single event or incident (serves as an illustration) use of words that sound like the thing they refer to (hiss/pop) theme, motif, symbol, character holds familiar and fixed place in culture prayer for inspiration to a god or muse (usually at the beginning) common character type that recurs throughout literature literal, dictionary definition of a word repetition of sounds repetition of similar vowel sounds recurring structure, contrast, etc. that develops a work’s major theme (mocking bird) adjective or phrase that describes a prominent feature of a person or thing character who illuminates qualities of another character by means of contrast a play on words exploiting similar sounds with distinctly different meanings clash of discordant or harsh sounds a common expression that has acquired a meaning different from its literal one presents the total range of thoughts, memories, associations of a character a general statement of an aspect of literary work that can be substantiated short narrative that illustrates a moral by means of allegory any composition not written in verse vantage point from which author presents the action of the story unrhymed iambic pentameter word choice the manner of speaking an author uses; revealed in attitude toward subject similar or like grammatical structures (to be or not to be) two consecutive lines that rhyme group of American writers in the 1950s & ‘60s-bohemian counterculture poem that laments the death of someone/something 17th-century poets who combined direct language with ingenious images/conceits overstatement--exaggeration sentence structure; pattern of formation or phrases. unique conscious and unconscious choices an author makes intended to instruct or education serious lyric poem to commemorate an occasion or person humorous and often satirical imitation of a particular work or author use of decorous language to express vulgar or unpleasant ideas, events, actions attributing human feeling or motivation to nonhuman object (esp. in nature) Latin for in the middle of things; starting a narrative in the middle of the action