Year 2 Teaching Sequence xxx
advertisement

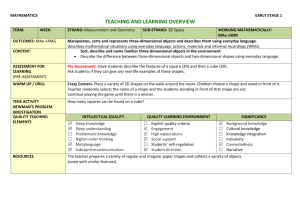
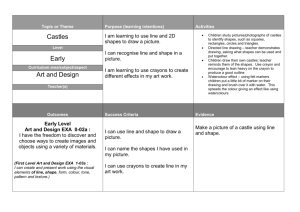
Year 2 Teaching Sequence summer D6 – Using lists, tables and diagrams to sort shapes (two days) Prerequisites: Begin to use lists, tables and diagrams to sort objects; explain choices using appropriate language, including ‘not’ (see teaching sequence D4) Visualise common 2D shapes, identify from pictures in different positions and orientations (see teaching sequence S6 and oral and mental starter bank D6) Sort, make and describe 2D shapes, referring to their properties (see teaching sequence S6) Recognise that a right angle is a quarter turn (see teaching sequence S6) Overview of progression: Children sort irregular and regular 2D shapes into triangles, pentagons and hexagons. Shapes are also sorted according to whether or not they have at least one right angle. Chn guess how shapes are sorted and suggest their own criteria for sorting them. Note that this sequence follows on from Teaching sequence S6 about 2D shapes and right angles. Note that pairs of headings in Carroll diagrams are mutually exclusive (the opposite of one another), thus using the word ‘not’. This means that all objects will be in one column or the other. Watch out for children who only recognise regular pentagons and hexagons, equilateral triangles as triangles, or only recognise triangles, squares and rectangles sitting on one side. In this sequence they meet a range of pentagons and hexagons in order to clarify what makes a shape a pentagon or hexagon. © Original teaching sequence copyright Hamilton Trust, who give permission for it to be adapted as wished by individual users. Y2 Maths TS_D6 – Sum – 2days Objectives: Use lists, tables and diagrams to sort objects; explain choices using appropriate language, including ‘not’ Whole class Group activities Paired/indiv practice Resources Hoops and labels as opposite ‘Dotty’ paper (spots arranged as on a geoboard) Activity sheet of 2D shapes (see resources) Scissor and glue sticks Ask chn to choose to draw a shape with three, five or six sides on their whiteboards. They must draw it so that the sides aren’t the same length! Label three hoops ‘triangles’, ‘pentagons’ and ‘hexagons’. Chn swap boards with a partner who must place it in the correct hoop. What makes a hexagon a hexagon? Chn retrieve their boards. Challenge them to draw the oddest looking hexagons that they can! Share some of these with the whole class. Include concave examples (or draw one), e.g. Group of 4-5 children Ask chn to draw as many different looking pentagons as they can on ‘dotty paper’ and then to cut them out. Together sort them into those which have right angles and those which do not. Easier: Ask chn to draw three-sided, four-sided, five-sided and six sided shapes and then sort them into ‘pentagons’ and ‘not pentagons’. Chn cut out a range of 2D shapes (see Activity sheet) and sort them using the following diagram: Is a hexagon Is not a hexagon Draw a range of 2D shapes on the IWB such as the following: Group of 4-5 children Show chn a range of plastic 2D shapes. How could we sort these into two sets so that every shape can go into one or the other set? Draw out using the language of ‘not’, so shapes can only be in one set or the other. Try out different suggestions. Easier/Harder: Chn will need more or less help with suggestions according to their attainment in this area. Chn cut out a range of 2D shapes (see Activity sheet) and sort them using the following Carroll diagram: Has at least Has no right one right angles angle Start to sort them by dragging them into two sets, regular and irregular, but not telling the chn how you are doing this. How do you think I’m sorting Harder: Chn draw two extra shapes in each column. Activity sheet of 2D shapes (as session one) Scissor and glue sticks Angle checkers made in teaching sequence S6 They can use their angle checkers made in teaching sequence S6 to help. © Original teaching sequence copyright Hamilton Trust, who give permission for it to be adapted as wished by individual users. Y2 Maths TS_D6 – Sum – 2days these shapes? Point to a shape you have not yet sorted. Where do you think I’ll put this shape? Why? Draw out that the shapes in one set all have sides of the same length, but the others do not. Remind chn that these are called regular and irregular shapes. Look at the regular shapes. How could I sort these? (Has a right angle does not have a right angle.) Sort both sets according to the same. We have sorted these shapes in two ways at once. Add labels to show chn the resulting Carroll diagram. Harder: Chn sort the shapes into those which are hexagons and those which are not. They then tick all those shapes with right angles and place the shapes in the following Carroll diagram: Has at Has no least one right right angles angle Is a hexagon Is not a hexagon © Original teaching sequence copyright Hamilton Trust, who give permission for it to be adapted as wished by individual users. Y2 Maths TS_D6 – Sum – 2days