LA Maths - ES1 - Plan 4 - Glenmore Park Learning Alliance
advertisement
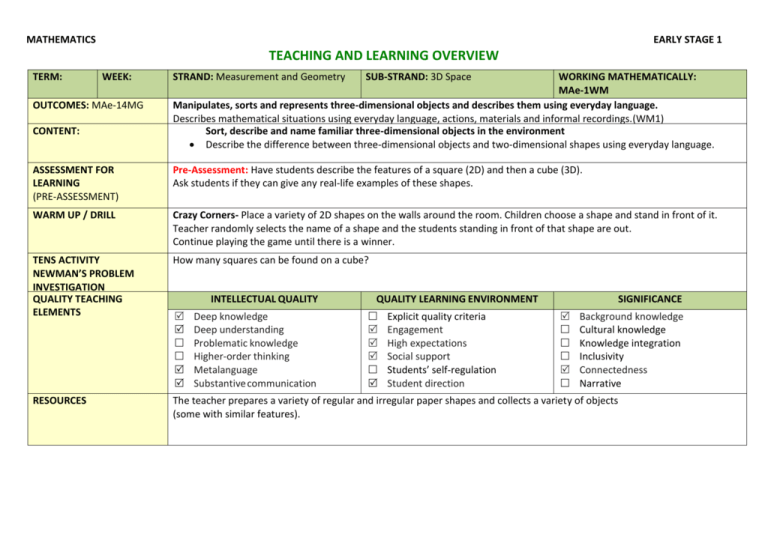
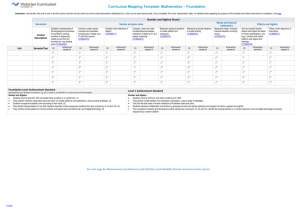
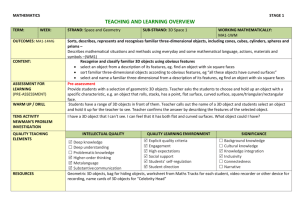
MATHEMATICS EARLY STAGE 1 TEACHING AND LEARNING OVERVIEW TERM: WEEK: OUTCOMES: MAe-14MG CONTENT: STRAND: Measurement and Geometry SUB-STRAND: 3D Space WORKING MATHEMATICALLY: MAe-1WM Manipulates, sorts and represents three-dimensional objects and describes them using everyday language. Describes mathematical situations using everyday language, actions, materials and informal recordings.(WM1) Sort, describe and name familiar three-dimensional objects in the environment Describe the difference between three-dimensional objects and two-dimensional shapes using everyday language. ASSESSMENT FOR LEARNING (PRE-ASSESSMENT) Pre-Assessment: Have students describe the features of a square (2D) and then a cube (3D). Ask students if they can give any real-life examples of these shapes. WARM UP / DRILL Crazy Corners- Place a variety of 2D shapes on the walls around the room. Children choose a shape and stand in front of it. Teacher randomly selects the name of a shape and the students standing in front of that shape are out. Continue playing the game until there is a winner. TENS ACTIVITY NEWMAN’S PROBLEM INVESTIGATION QUALITY TEACHING ELEMENTS How many squares can be found on a cube? RESOURCES The teacher prepares a variety of regular and irregular paper shapes and collects a variety of objects (some with similar features). INTELLECTUAL QUALITY Deep knowledge Deep understanding Problematic knowledge Higher-order thinking Metalanguage Substantive communication QUALITY LEARNING ENVIRONMENT Explicit quality criteria Engagement High expectations Social support Students’ self-regulation Student direction SIGNIFICANCE Background knowledge Cultural knowledge Knowledge integration Inclusivity Connectedness Narrative TEACHING AND LEARNING EXPERIENCES WHOLE CLASS INSTRUCTION MODELLED ACTIVITIES Explicitly communicate lesson outcomes and work quality Define and reinforce metalanguage used in the unit. Shape,3D Object, Edge- Corner, Face, Flat and Fat-. Sorting and Classifying (Two and Three-Dimensional Space). Show students a variety of 2D and 3D models. Ask volunteers to find examples of the models within the classroom. Explain that they should all find one that is ‘flat’ (i.e. A representation of a 2D shape) and one that is ‘fat’ (i.e. A representation of a 3D object). Volunteers are asked to sort the shapes and objects into groups e.g. rough or smooth, colour, size, shape. Students are asked to explain their grouping. Volunteers are then asked to sort the shapes and objects in a different way. For example, if the students sort them according to their colour the teacher could ask ‘If these shapes and objects were all red, how would you sort them?’ Introduce the idea that they could be sorted based on how many corners or faces they have. GUIDED & INDEPENDENT ACTIVITIES LEARNING SEQUENCE Pre Foundation Skills Play-dough Objects - Students will use 2D and 3D models to help them make at least three playdough objects. Ask the students to show their work to a friend and try to name the objects. LEARNING SEQUENCE In small groups, students take turns to sort the shapes and objects for others to determine and explain how they have been sorted. Possible questions include: How many different ways can you sort the shapes? Is this shape a square, a rectangle or a triangle? How do we know? How are these objects (two rectangles) the same or different? Can you name each object? How are these objects (a rectangle and a rectangular prism) different? Investigation: Ask students to look for matching 2D shapes and 3D objects at home for homework. Volunteers will discuss the objects they found. In the discussion, ask students how many corners or faces the objects had, or if the objects had curved or flat faces. Assessment: Have different students role-play being the teacher and ‘teach’ the other students about the characteristics of different 3D and 2D objects. Barrier Shapes - In pairs, each student is given an identical set of three-dimensional objects e.g. 1 cube, 3 rectangular prisms, 1 cone, and 2 cylinders. Student A creates a construction using the objects and conceals it. They describe it to Student B who attempts to produce the same construction. Students compare constructions, swap roles and repeat the activity. Possible questions include: Could your partner follow your instructions? What 3D objects did you use, describe your construction. How did you build it? Student engagement: Achievement of Outcomes: Resources: Follow up: ES1 LEARNING SEQUENCE Extension S1 EVALUATION & REFLECTION