HOW TO READ THE DAILY STOCK MARKET REPORT High Low
advertisement

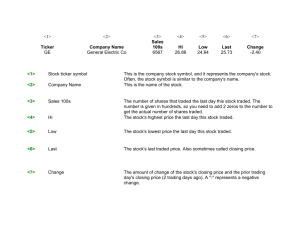
HOW TO READ THE DAILY STOCK MARKET REPORT Stock Div. 843/4 541/2 Quak Ot High Low 1.60 2.1 Yld% 17 P-E Ratio The price of Quaker Oats shares in current year. Annual dividend per share in dollars to stockholders Yield = Div. x 100 / closing price Price-earnings ratio: Number of shares In day that the number of times changed hands (54,600). the current market value of the company exceeds its annual profits. Most institutional investment takes place in stocks traded on the two major exchanges: the New York Stock Exchange, where stocks of the nation's largest companies are traded, and the smaller American Stock Exchange, also located in New York. In addition, there are half a dozen regional exchanges around the country that trade many of the same stocks listed on the major exchanges. But the stocks of the overwhelming number of companies, the tens of thousands of small corporations that have publicly traded stocks, are not sold on any stock exchange floor. They are sold by individual brokers "over the counter." The stock exchanges do not handle new issues of stock. When a company wishes to issue new shares of stock, it negotiates a sale of the stock to an investment bank, or, if it is a major corporation raising a very large amount of money, to a group of investment banks referred to as a consortium. Investment banks then sell the stocks through brokers to the public. If there is a bullish market for the stock, an investment bank can sell the stock for a great deal more than it paid the issuing company. If there is not much demand for the stock, the bank can lose money. Small "start-up" companies are frequently financed by venture capitalists, financiers who provide funds for promising new ventures in return for part ownership in the company. If the company succeeds well enough to "go public," that is, make a stock offering to the general public, the venture capitalist Sales 100s 546 High Low Close 751/2 741/2 75 Net Chg. + 1/ 2 Net price change from previous day's closing price (expressed as a fraction of a dollar). can reap rewards many times the amount of the capital invested in the company. Although the stock exchanges do not trade new issues of stock, they are important to the ability of companies to raise investment capital. Investors would be reluctant to buy stock in a company if there were no ready way to dispose of it when they want to get their money out. The efficiency of the U.S. stock market is important to the dynamism of our economy. However, excessive speculation in the stock market can create big problems, as it did in the financial collapse of 1929. Running with the bulls is exciting, but a bull can cause havoc in a china shop economy. For Thought 1. Are shares of ownership of most business organizations traded in the stock market? What types of businesses are traded there? 2. Which of the functions of business firms are most affected by the stock market? How? 3. Should the Securities and Exchange Commission reduce the amount of speculation in the stock market by prohibiting investors from buying stock on credit, paying only a fraction in cash and pledging the stock as collateral on the balance owed? Why should such "buying on the margin" be allowed or why should it be prohibited? 113 What Determines a Firm's Profits? fixed costs production costs which do not change with changes in the quantity of output. The objective of producers in all types of business organizations is to make the largest possible profit. Profit is the difference between the revenue a firm takes in and the costs it incurs. For the farmers in financial difficulty, their profits were negative—costs were greater than revenues. Like other producers, farmers try to maximize profits or minimize losses. This is accomplished by producing the most profitable quantity of output with the resources available. We will use a farm operation to illustrate how costs and revenue are determined and how they determine profits. Costs To illustrate how a firm's costs affect production decisions we will use the example of a chicken farm. A chicken farm with 100,000 laying hens might have three employees and an owner-manager. A large percentage of the hens have to be replaced each year because hens have a limited time of productivity. During its productive span a hen will lay, on the average, about 250 eggs a year. Modern chicken farms keep the hens in cages with automated feeding equipment. In contrast to farms that grow crops, they do not need much land, just a few acres. As with other businesses, chicken farms have two categories of costs: fixed and variable. Fixed costs are those A major cost of chicken farming is hen depreciation. 114