Unit 4 – DNA Technology and Genomics Part II
advertisement

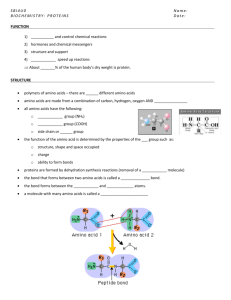
Unit 3 Biology Biomacromolecules Part III: Proteins Guiding Questions 1. Why are proteins important (what are their jobs)? 2. How many functions do most proteins have? 3. What does the acronym “TEACHERS” stand for? 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. How are polypeptides formed? What are the monomers for polypeptides? Why are amino acids essential biomolecules? How many amino acids are there? How many amino acids can humans actually make? What are essential amino acids? 10. What does the acronym “PONCH” stand for? 11. 12. 13. 14. What is the basic structure of all amino acids? What is responsible for the differing chemical properties of different amino acids? What form do amino acids exist in when they are present in the cytosol? What are dipolar ions called? 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. What are some examples of R groups of different amino acids? Which amino acid contains sulphur in the R group? How many amino acids have R groups that make them hydrophobic? How many amino acids have R groups that make them hydrophilic? Where are hydrophilic amino acids generally found and why? Where are hydrophobic amino acids found and why? 21. In the formation of polypeptides what type of bonds result from the process of condensation polymerisation? 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. What chemical group is found at the N terminus of a polypeptide? What chemical group is found at the C terminus of a polypeptide? Which chemical group is conventionally depicted to the left when drawing polypeptides? What are amino acids referred to once they are linked by peptide bonds? What are chains of less than 20 – 30 amino acid residues referred to as? What are chains of greater than 20 – 30 amino acid residues referred to as? What is the term protein reserved for? What unit is used to measure the size of proteins? 30. 31. 32. 33. What allows proteins to have biological functionality? How many polypeptides does a monomeric protein contain? How many polypeptides does a multimeric protein contain? What dictates the final shape of multimeric proteins? 34. Name an example of a multimeric protein? 35. How many polypeptides does haemoglobin have in total? How many different types of polypeptides does it have? 36. What are the four levels of protein structure? 37. What is the primary structure of a protein? 38. How is the order of amino acids in a polypeptide determined? 39. What are three amino acids of structural importance? 40. What is special about each of these amino acids? 41. Why do different parts of a polypeptide assume different geometric arrangements? 42. What are the three types of secondary structure? 43. Are beta sheets parallel or perpendicular to the protein sheet? 44. What areas of a polypeptide are referred to as random coils? 45. Where are random coils commonly found? 46. 47. 48. 49. What is the conformation of a protein? How is the final shape determined? Where are covalent bonds formed? Why do hydrophobic R groups interact? 50. 51. 52. 53. 54. 55. 56. What are the two broad groups of proteins based on their tertiary structure? What gives fibrous proteins their highly ordered repetitive structure? Is tertiary structure important in these proteins? What are some examples of fibrous proteins? What is the structure of globular proteins? What is the purpose of the irregularly structured regions of protein? What is an example of a globular protein? 57. What is the quaternary structure of a protein?