Atomic Structure - FW Johnson Collegiate
advertisement

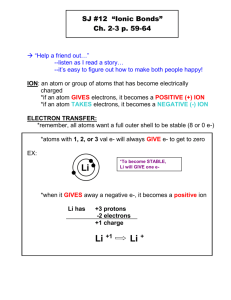
SCIENCE 10: Chemical Reactions – Atomic Structure 1. Terms: a) Periodic table: b) Atomic #: c) Atomic Weight (Mass #): d) Ion: e) Bohr Diagram: 2. How would you find out the number of ******** in an atom? a) Protons: b) Electrons: c) Neutrons: 3. Bohr Diagrams: a) 1st orbit = 2 electrons maximum b) 2nd orbit = 8 electrons maximum c) 3rd orbit = 8 electrons maximum d) A lower orbit must be FULL before electrons can be placed into a higher orbit Example: Carbon: Magnesium: 4. Atomic Structure Chart: Complete the missing information in the chart ELEMENT Atomic # Mass # Hydrogen SYMBOL # PROTONS # ELECTRONS # NEUTRONS 8 8 8 BOHR DIGRAM POSSIBLE ION Na Cl1- Fluorine S 15 15 16 Li1+ 5. Ionic Compounds: (p.192) a) Metals: b) Non-metals: c) Valence #: Metals & non-metals combine to form ionic compounds. Metals ions lose electrons to form positive ions. Non-metals gain electrons to form negative ions. The resulting compound must be electrically neutral: the positive charges must equal the negative charges. Example: magnesium combines with chlorine to form the ionic compound magnesium chloride Mg2+ and Cl1each magnesium ion gains 2 electrons two chlorine ions are needed since each loses only 1 electron result is MgCl2 2+ 1- ?(2+) + ?(1-) = 0 Mg Cl 1(2+) + 2(1-) = 0 MgCl2 some metals can form more than one type of ion. A Roman numeral in round brackets is used to show the charge on the metal ion. (p.195) Example: The element copper forms two different compounds with chlorine. Chlorine always forms a 1- ion. Copper can form either a 1+ ion or a 2+ ion. CuCl = copper (I) chloride CuCl2 = copper (II) chloride Naming Ionic Compounds: (p.194) o Metal name first, non-metal name second o Change the ending of the non-metal to “ide” 6. Polyatomic Compounds: (p.196) a) polyatomic ion: o A table of polyatomic ions can be found on your Periodic Table of Ions. o If more than one polyatomic ion is needed to balance the positive and negative charges, then the polyatomic ion is written in brackets and the number placed after and lower. o Don’t change the ending of the non-metal polyatomic ions. Examples: Calcium ions (Ca2+) combine with Carbonate ions (CO32-) to form calcium carbonate CaCO3 Sodium ions (Na+) combine with Carbonate ions (CO32-) to form Sodium carbonate Na2CO3 Calcium ions (Ca2+) combine with Chlorate ions (ClO3-) to form Calcium chlorate Ca(ClO3)2 7. Molecular Compounds: (p.201) a) Ionic compound: b) Molecular compound: c) Covalent bond: d) Diatomic molecules: Prefixes are used when different molecular compounds can be formed by the same elements: Example: 1 carbon atom combined with 1 oxygen atom = carbon monoxide 1 carbon atom combined with 2 oxygen atoms = carbon dioxide 8. Predict the name and formula for each of the following pairs of elements: a) lithium & fluorine l) potassium & sulphate b) magnesium & chlorine m) nickel (II) & silicate c) zinc & bromine n) ammonium & oxygen d) aluminum & oxygen o) titanium (IV) & sulphite e) iron (III) & chlorine p) sodium & dihydrogen phosphate f) silver & phosphorus q) carbon & 1 oxygen g) tin (II) & oxygen r) carbon & 2 oxygen h) lead (IV) & bromine s) carbon & 4 fluorine i) copper (I) & sulfur t) sulfur & 3 oxygen j) sodium & acetate u) sodium & nitrate k) calcium & hydroxide v) sodium & nitrite