LCME ED 10 Topics
advertisement
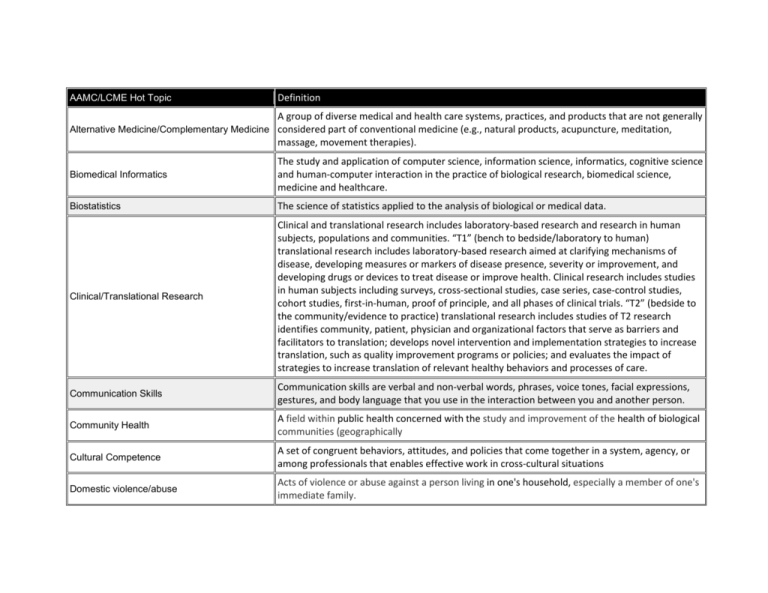
AAMC/LCME Hot Topic Definition A group of diverse medical and health care systems, practices, and products that are not generally Alternative Medicine/Complementary Medicine considered part of conventional medicine (e.g., natural products, acupuncture, meditation, massage, movement therapies). Biomedical Informatics The study and application of computer science, information science, informatics, cognitive science and human-computer interaction in the practice of biological research, biomedical science, medicine and healthcare. Biostatistics The science of statistics applied to the analysis of biological or medical data. Clinical/Translational Research Clinical and translational research includes laboratory-based research and research in human subjects, populations and communities. “T1” (bench to bedside/laboratory to human) translational research includes laboratory-based research aimed at clarifying mechanisms of disease, developing measures or markers of disease presence, severity or improvement, and developing drugs or devices to treat disease or improve health. Clinical research includes studies in human subjects including surveys, cross-sectional studies, case series, case-control studies, cohort studies, first-in-human, proof of principle, and all phases of clinical trials. “T2” (bedside to the community/evidence to practice) translational research includes studies of T2 research identifies community, patient, physician and organizational factors that serve as barriers and facilitators to translation; develops novel intervention and implementation strategies to increase translation, such as quality improvement programs or policies; and evaluates the impact of strategies to increase translation of relevant healthy behaviors and processes of care. Communication Skills Communication skills are verbal and non-verbal words, phrases, voice tones, facial expressions, gestures, and body language that you use in the interaction between you and another person. Community Health A field within public health concerned with the study and improvement of the health of biological communities (geographically Cultural Competence A set of congruent behaviors, attitudes, and policies that come together in a system, agency, or among professionals that enables effective work in cross-cultural situations Domestic violence/abuse Acts of violence or abuse against a person living in one's household, especially a member of one's immediate family. End-of-Life Care The care provided to a person in their final stages of life. Epidemiology The branch of medicine that deals with the incidence, distribution, and control of diseases. Evidence Based Medicine The judicious use of the best current available scientific research in making decisions about the care of patients. Global Health Issues Collaborative trans-national research and action for promoting health for all Health Care Financing Branch of finance that helps patients and health care beneficiaries pay for medical expenses in the short and long terms Health Care Quality Improvement The extent to which health services provided to individuals and patient populations improve desired health outcomes. Health Care Systems The complete network of agencies, facilities, and all providers of health care in a specified geographic area. Health Disparities The inequalities that exist when members of certain population groups do not benefit from the same health status as other groups. Human Development/Life Cycle The study of how people develop on physical, intellectual and social levels. Human Sexuality/Sexual Functioning The sum of the physical, functional, and psychologic attributes that are expressed by one's gender identity and sexual behavior Medical Ethics The moral conduct and principles that govern the medical profession Medical Genetics The study of the etiology, pathogenesis, and natural history of diseases and disorders that are at least partially genetic in origin. Medical Humanities An interdisciplinary field of medicine which includes the humanities (literature, philosophy, ethics, history and religion), social science (anthropology, cultural studies, psychology, sociology), and the arts (literature, theater, film, and visual arts) and their application to medical education and practice. Medical Jurisprudence All matters which may bring the physician into contact with the law. Medical Socioeconomics The position of an individual on a social-economic scale that measures such factors as education, income, type of occupation, place of residence, and, in some populations, heritage and religion and how SES relates to disease. Nutrition The role of nutrition in chronic disease, including possible prevention or remediation by addressing nutritional deficiencies before resorting to drugs Occupational health/medicine The branch of medicine that deals with the prevention and treatment of diseases and injuries occurring at work or in specific occupations. Pain Management Pharmacological, nonpharmacological, and other approaches to prevent, reduce, or stop pain sensations. Palliative Care Medical care provided by physicians, nurses and social workers that specializes in the relief of the pain, symptoms and stress of serious illness. Patient safety The reporting, analysis, and prevention of medical error that often leads to adverse healthcare events Population-based Medicine The health outcomes of a group of individuals, including the distribution of such outcomes within the group Prevention/health maintenance A pattern of nursing and medical care that focuses on disease prevention and health maintenance. Rehabilitation/Care of the disabled A treatment or treatments designed to facilitate the process of recovery from injury, illness, or disease to as normal a condition as possible Research Methods The diligent inquiry or examination of data, reports, and observations in a search for facts or principles Substance Abuse use of a substance that modifies mood or behavior in a manner characterized by a maladaptive pattern of use. Women's Health The effect of gender on disease and health that encompasses a broad range of biological and psychosocial issues.