Physics Review – Mirrors and Lenses
advertisement

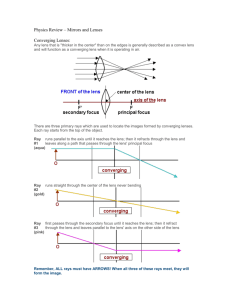
Physics Review – Mirrors and Lenses Diverging Lenses: Any lens that is "thinner in the center" than on the edges is called a concave lens and will function as a diverging lens when operating in air. The point where rays which entered the lens parallel to its axis are brought to a focus in front of the lens is called the principal focus. This position is usually labeled F in ray diagrams. A similar point the same distance behind the lens is called the lens' secondary focus, F'. When the actual rays of light diverge after passing through the lens, the image formed by the intersection of their "dotted back segments" is called a virtual image. Virtual images are always upright images which are "trapped" inside the lens. Since the actual rays of light do NOT form these images, virtual images are also known as "cool" images. This type of image can NOT be projected onto a screen. There are three primary rays which are used in ray diagrams to locate images formed by diverging lenses. Each of these rays start on the top of the object. There are three primary rays which are used in ray diagrams to locate images formed by diverging lenses. Each of these rays start on the top of the object. Ray runs parallel to the axis, refracts through the lens so that, when dotted back, it passes #1 through the principal focus (aqua) Ray #2 runs straight through the center of the lens never bending (gold) Ray aims for the secondary focus, refracts through the lens and runs off parallel to the axis on #3 the other side of the lens (pink)