Lenses and the Formation of Images
advertisement

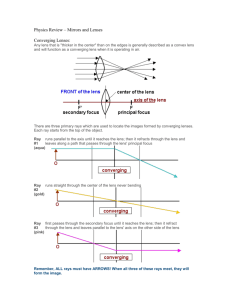
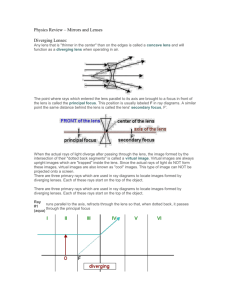
Lenses and the Formation of Images Basic Lens Shapes Converging Lens -thickest in the middle (thinnest at edge) -causes parallel light rays to converge (come together) through a single point after refraction Diverging Lens -thinnest in the middle (thickest at edge) -causes incident parallel rays to spread apart after refraction • We will only study the incident ray coming into the lens and the ray leaving the lens (in actuality there are two refractions in a lens; air to glass, glass to air) Converging Lenses Words 2F’ 2F Converging Lenses Words Optical Centre (O)- Centre of the Lens Principal Axis (PA)- The line through the optical centre that is perpendicular to the central dashed line of the lens Principal Focus (F)-the point on the PA of a lens where light rays parallel to the PA converge after refraction Secondary Principal Focus (F’)- the focus that is on the sam side of the lens relative to the incident rays 2F- twice the distance from the principal focus 2F’-twice the distance from the secondary principal focus Diverging Lens Words 2F 2F’ -if you project the diverging rays backward off of a diverging lens, it looks as if they come from a virtual focus, this point now becomes the principal focus Secondary Principal Focus (F’)-now on the other side of the lens where the rays actually diverge Converging vs. Diverging Lenses Converging Lens -brings parallel light rays together through a focus after refraction Diverging Lens -spreads parallel light rays apart after refraction so that it looks as though they have come from a virtual focus -the principal focus is on -the principal focus is on the OPPOSITE side of the same side of the the lens as the incident lens as the incident rays rays What affects what an image will look like? • The type of lens (converging or diverging) • The location of the object With lenses, we will use ray diagrams to draw incident rays and refracted rays. Emergent rays-the ray that leaves the lens, refracted as it goes from the lens back to the air • In a thin prism, the emergent ray is almost unaffected by the presence of the prism • We will work with thin prisms. Thick Prism Thin Prism How to locate the image in a converging Lens A ray parallel to the principal axis is refracted through the principal focus. • A ray through the F’ is refracted parallel to the principal axis. • A ray through O continues straight through without being refracted • Where the two refracted lines cross, the image is produced. Object beyond 2F’ • • • • Smaller Inverted Between F and 2F Real Object at 2F’ • • • • Same Size Inverted At 2F Real Object between F’ and 2F’ • • • • Larger Inverted Beyond 2F Real Objects beyond 2F’ -the image is smaller than the object and between 2F and F -as you move slowly toward the lens, the image gets larger and larger -eventually the image and the object are the same size when the object is located at 2F’ the image would be at 2F Object at F • No clear image formed Object between F’ and the Lens • • • • Larger Upright Behind the Lens Virtual