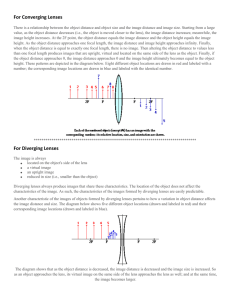
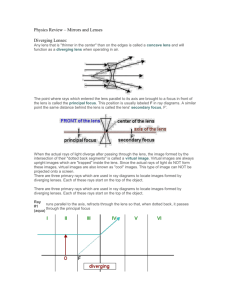
Here are three rules for ray tracing with converging lenses
advertisement

Ray tracing for lenses Objectives • Draw a ray diagram that shows refraction through a thin convex lens. • Predict the location and properties of an image created by a thin lens using a ray diagram. Physics terms • refraction • ray Essential question Lenses create images. How can you predict where the image will be and what it will look like? Use ray tracing to locate the image graphically. Ray tracing Previously, you used ray diagrams to predict where an image would appear when using a mirror. You can do the same thing with lenses! Converging lenses Here are three rules for ray tracing with converging lenses: Rule 1 Incident rays parallel to the optical axis refract through the far focal point. Converging lenses Here are three rules for ray tracing with converging lenses: Rule 1 Incident rays parallel to the optical axis refract through the far focal point. To draw accurate ray diagrams for lenses, sketch the rays as if the refraction occurs at the centerline of the lens. Converging lenses Here are three rules for ray tracing with converging lenses: Rule 2 Incident rays passing through the center of the lens pass straight through the lens undeflected. Converging lenses Here are three rules for ray tracing with converging lenses: Rule 3 Incident rays passing through the near focal point refract parallel to the optical axis. Converging lenses Here are three rules for ray tracing with converging lenses: Rule 3 Incident rays passing through the near focal point refract parallel to the optical axis. The image of any point on the object is formed where the refracted rays from that point intersect. Converging lenses Drawing ray diagrams allows us to predict the image properties. What are the properties of the image in the ray diagram on the right? Is it . . . • reduced or enlarged? • upright or inverted • real or virtual? Converging lenses This image is: • reduced in size • inverted • real Converging lenses How do you know that this is a real image? Converging lenses How do you know that this is a real image? A real image is formed where light rays actually intersect. Real images like this one can be projected on a screen. Converging lenses The image of any point on the object is formed where ALL the refracted rays from that point intersect. These 3 rays are traced simply because they are easy to construct. Converging lenses converging lens Every light ray from this treetop that passes through this lens will converge at the same point on the image. real image object Investigation Parallel rays never intersect. If rays leaving the lens are parallel to each other, there is NO IMAGE. Which object distance produces no image? Investigation Sometimes, to find where the rays intersect, you have to trace rays backwards on a ray diagram. These backwards light rays are virtual rays, represented with dashed lines. Diverging lenses Ray tracing can also be used to predict the location of an image produced by a diverging lens. Diverging lenses There are three rules for ray tracing with diverging lenses: Rule 1 Incident rays parallel to the optical axis refract as if they came from the near focal point. Diverging lenses There are three rules for ray tracing with diverging lenses: Rule 2 Incident rays passing through the center of the lens refract straight through the lens undeflected. Diverging lenses There are three rules for ray tracing with diverging lenses: Rule 3 Incident rays directed towards the far focal point refract out parallel to the optical axis. Diverging lenses Where is the image? Notice that the rays on the far side of the lens diverge, so the image cannot be locate there. Diverging lenses Where is the image? The image is located where it appears as if the rays intersected. Diverging lenses Remember: To find where the rays intersect, you may have to trace rays backwards on a ray diagram. These backwards light rays are virtual light rays. Represent them with a dashed line. Diverging lenses What are the properties of the image formed by the diverging lens represented in the diagram? • real or virtual? • upright or inverted • reduced or enlarged? Diverging lenses This image is: • virtual • upright • reduced in size Diverging lenses How do you know that this is a virtual image? Diverging lenses How do you know that this is a virtual image? • The real light rays never converge to a point. • The intersecting rays are virtual rays. • For a lens, this means the image is on the same side as the object. Diverging lenses Test the diverging lens. To view the virtual image, look through the diverging lens at the object. You should see an image that is: • virtual • upright • reduced in size Assessment 1. Which letter below correctly identifies the location of the image in this ray diagram? Assessment 1. Which letter below correctly identifies the location of the image in this ray diagram? Answer: D Assessment 2. An object is placed 30 cm away from a converging lens with a focal length of 20 cm. What are the properties of the image that is created? Use ray tracing to figure out the image properties. Assessment 2. An object is placed 30 cm away from a converging lens with a focal length of 20 cm. What are the properties of the image that is created? Use ray tracing to figure out the image properties. The image is: • real • magnified • inverted