Nome Completo: Ana Valéria Colnaghi Simionato

Sociedade Brasileira de Espectrometria de Massas – BrMASS
Drug Analysis
Simultaneuos determination of rosuvastatin (RVT) and ezetimibe (EZT) in human plasma using liquid-liquid extraction and high-performance liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry: Application to a bioequivalence study.
Kátia I. F. Pastre 1 , Paulo A. R. Galvinas 1
Armando 1 , Simone G. Schramm 1
, Camila L. Guimarães
, Washington M. Silva 1
Olívia M. Amorim 1 , Kleber P. A. Junior
Watanabe
1 , Loretta A. A. Paoleschi
1
1 , Yara P.
, Américo A. S. Neto
1 , Cintia P.
1 ,
katia.pastre@magabi.com.br
1 Magabi Pesquisas Clínicas e Farmacêuticas Ltda. Rodovia Pres. Castello
Branco, km 35,6 - Itaqui – Itapevi/SP - Brasil
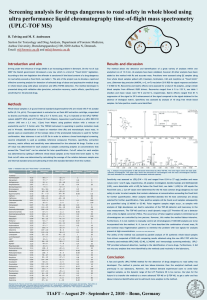
Objective: Development of a specific and sensitive, high performance liquid chromatography–mass spectrometric (LC–MS/MS) assay, for simultaneous determination of RVT and EZT in human plasma samples from bioequivalence studies.
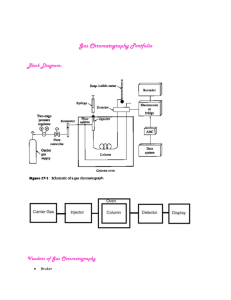
Method: A plasma aliquot was liquid-liquid extracted with diethyl ether/hexane. After dryness, the samples were reconstituted with acetonitrile/water (60/40; v/v) + Formic
Acid 8 mM and 20 uL were injected into the HPLC system. The chromatography was performed using a Phenomenex, Synergi, Polar RP, 4um (50 x 4,6 mm i.d.) analytical column, operating at 40°C. The analytes (RVT and EZT) and their internal standards
(Rosuvastatin-D6, RVT-D6 and Ezetimibe-D4, EZT-D4, respectively) were eluted with acetonitrile/water + Formic Acid 20mM (52/48; v/v). The total run time was 3.0 min.
The analytes retention time were 1.3 min (RVT and RVT-D6) and 2.0 min (EZT and
EZT-D4). The analysis was performed in negative electrospray. The multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) detection mode was employed for EZT (m/z 408.1/271.1), RVT (m/z
480.0/340.2) and their respective internal standards EZT-D4 (m/z 412.2/271.1) and
RVT-D6 (m/z 486.2/346.2) for precursor and product ion fragments respectively.
Results: The analytes’ lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) were 0.100 ng/ml (EZT) and 0.300 ng/ml (RVT). The calibration curve was linear (1/x weighted) in the concentration range of 0.100 – 25.0 ng/ml and 0.300 – 75.0 ng/ml, respectively. Intrabatch precision and accuracy of the assay was measured at five quality control levels, also including LLOQ and diluted Quality Control. Inter and intra-batch precision for both analytes and IS were lower than 15%.
Conclusion: All current bioanalytical method validation requirements (ANVISA and
FDA) were achieved and it was applied for the quantification of biological samples from a bioequivalence study.
5º Congresso BrMass – 07 a 11 de Dezembro de 2013
![SUNSPOTS: mt − pt = a − b[Ep t+1 − pt] Let zt = mt − pt. Then zt = mt](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/018349753_1-c13b0b48398dd1be389310c631e0f1b9-300x300.png)