Biomes Vocabulary 1. Tundra – a treeless plain especially of arctic
advertisement

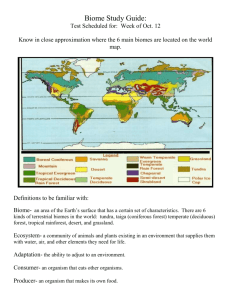
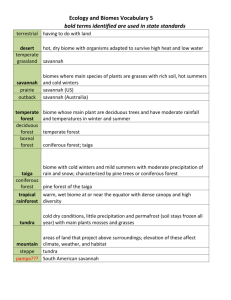
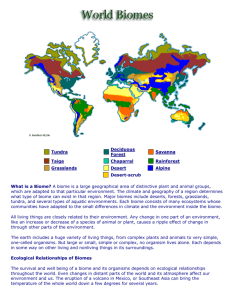
Biomes Vocabulary 1. Tundra – a treeless plain especially of arctic regions having a permanently frozen layer below the surface soil and plant life made up mostly of mosses, lichens, herbs, and very small shrubs. 2. Taiga or Coniferous Forest - the largest biome on earth that consist of cold woodland or forest, often on marshy land. 3. Rain Forest - an often tropical woodland with a high annual rainfall and very tall evergreen trees with tops forming a continuous layer. 4. Deciduous Forest / Temperate Forest- woodland that has a temperate climate with heavy rainfall and that usually includes numerous kinds of trees but differs from a tropical rain forest in having one or two very common major trees. 5. Desert - arid land with usually sparse vegetation; especially : such land having a very warm climate and receiving less than 25 centimeters (10 inches) of sporadic rainfall annually. 6. Grassland/Savanna - a tropical or subtropical grassland (as of eastern Africa or northern South America) containing scattered trees and drought-resistant undergrowth. Tundra is among Earth's coldest, harshest biomes. Tundra ecosystems are treeless regions found in the Arctic and on the tops of mountains, where the climate is cold and windy and rainfall is scant. Taiga is the biome of the needle leaf forest. Living in the taiga is cold and lonely. Coldness and food shortages make things very difficult, mostly in the winter. Taiga is the Russian word for forest and is the largest biome in the world. It stretches over Eurasia and North America. The taiga is located near the top of the world, just below the tundra biome. The winters in the taiga are very cold with only snowfall. The summers are warm, rainy, and humid. A lot of coniferous trees grow in the taiga. The taiga is also known as the boreal forest. Rainforest have four very distinct layers of trees in a tropical rain forest. These layers have been identified as the emergent, upper canopy, understory, and forest floor. Emergent trees are spaced wide apart, and are 100 to 240 feet tall with umbrella-shaped canopies that grow above the forest. 2. The upper canopy of 60 to 130 foot trees allows light to be easily available at the top of this layer, but greatly reduced any light below it. 3. The understory, or lower canopy, consists of 60 foot trees. This layer is made up of the trunks of canopy trees, shrubs, plants and small trees. There is little air movement. 4. The forest floor is usually completely shaded, except where a canopy tree has fallen and created an opening. Most areas of the forest floor receive so little light that few bushes or herbs can grow there. As a result, a person can easily walk through most parts of a tropical rain forest. 1. Deciduous Forest / Temperate Forest is composed of broad-leaf angiosperm trees like the oaks, maples, and beeches familiar to many Americans and Europeans. The forests exist best in moderate climates that are neither too hot nor too cold and neither too wet nor too dry. In addition to the temperate zone, deciduous forests are found in tropical and subtropical climates in open savannas and/or in closed forests. Tundra lands are snow-covered for much of the year, until summer brings a burst of wildflowers. The tundra is the simplest biome in terms of species composition and food chains. It also receives low amounts of precipitation, making the tundra similar to a desert. Tundra is found in the regions just below the ice caps of the Arctic, extending across North America, to Europe, and Siberia in Asia. Much of Alaska and about half of Canada are in the tundra biome. Deserts cover about one fifth of the Earth's surface and occur where rainfall is less than 50 cm/year. Although most deserts, such as the Sahara of North Africa and the deserts of the southwestern U.S., Mexico, and Australia, occur at low latitudes, another kind of desert, cold deserts, occur in the basin and range area of Utah and Nevada and in parts of western Asia. There are relatively few large mammals in deserts because most are not capable of storing sufficient water and withstanding the heat. Deserts often provide little shelter from the sun for large animals. Grassland/Savanna is temperate grassland with scattered trees (as oaks). A savanna is a rolling grassland scattered with shrubs and isolated trees, which can be found between a tropical rainforest and desert biome. Not enough rain falls on a savanna to support forests. Savannas are also known as tropical grasslands. They are found in a wide band on either side of the equator on the edges of tropical rainforests.