Worksheet 30 Key - Iowa State University
advertisement

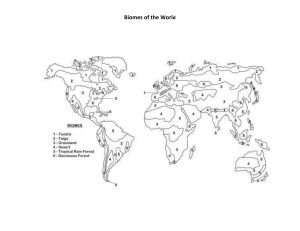
Worksheet 30 – Review for Exam 5 Supplemental Instruction Iowa State University Leader: Kirsten Karkow Course: Biol 211 - Wilsey Date: 4/16/2012 Define the following terms: Ecology Biome Ecotone Rain Shadow Studies the interactions of organisms and their environment. A major natural habitat (characteristic climate, flora, and fauna). Transitional biome Dry leeward side of a mountain Indicate which of the following statements are true: __F__ Climates are less variable inland. __T__ Regions that get direct sunlight will be warmer than regions that get indirect sunlight. __T__ Areas of tundra have too little moisture and sunlight to support tree growth. __F__ Areas closer to the equator will have more dramatic winters and summers. __T__ Equatorial areas have more consistent sunrise and sunset times. __T__ Ocean currents can make coastal climates warmer or cooler than they would be. Match the following biomes with their correct descriptions: Tundra, Alpine Tundra, Chaparral, Tropical Grassland, Temperate Forest, Desert, Tropical Forest, Coniferous Forest, Temperate Grassland Extremely wet regions with very diverse wildlife. TROPICAL (RAIN) FOREST Cold areas with wet and dry seasons. Evergreen shrubs are common. CHAPARRAL Dry, cold regions with conical trees. CONIFEROUS FOREST Moderate areas with four seasons. Bison and elk are common. TEMPERATE GRASSLAND Extremely cold areas occurring near sea level. Only dwarf plants may grow. TUNDRA Very hot and dry areas. Grasslands with sparse trees. TROPICAL GRASSLAND (SAVANNA) Extremely arid regions with CAM plants. DESERT Regions with moderate-abundant rainfall. Deer and turkey are common. TEMPERATE FOREST Very dry and cold areas occurring at high altitude. ALPINE TUNDRA Where do brackish biomes or estuaries occur? Freshwater-ocean transitions. Where do abyssal biomes occur? At the deepest ocean depths. What marine biome contains the most diverse wildlife? Coral reefs. Answer the following multiple choice questions: 1. If you tag 100 cows, come back two weeks later, and find that 70 out of the 200 you counted have tags, what is the approximate population size of that herd? a. 140 b. 210 c. 285 d. 305 Supplemental Instruction 1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center 294-6624 www.si.iastate.edu 2. The distribution occurring when the negative interactions and positive interactions between members of the same species is… a. Uniform distribution b. Random distribution c. Clumped distribution 3. Which of the following does not affect the reproductive rate of a population? a. At what age reproduction begins b. At what age reproduction ends c. Frequency of reproduction d. How many offspring are produced each time e. Trick question, they all do 4. Which type of survivorship curve do humans display? a. Type I b. Type II c. Type III Define the following terms: Demography Discrete Generations Overlapping Generations Growth Rate Net Reproductive Rate Intrinsic Rate of Increase Carrying Capacity R-selected Species K-selected Species Exponential Population Growth Logistic Population Growth Statistical study of populations. Includes birth rates, death rates, migration, sex ratios, and age structures. Adults die before the next generation is born. When individuals of many generations are alive at once. R = B - D. Describes whether a population is growing (R > 0), declining (R < 0), or at equilibrium (R = 0). R0 = N2/N1. The average number of offspring an individual will produce in his/her lifetime. The population is growing if R0 > 1. Rmax. Growth rate under ideal conditions (no environmental limits). K, the maximum population an environment can sustain. Display rapid initial growth, but unable to sustain N around K. Slower initial growth, but can sustain N around K. J-shaped (unlimited, continually accelerating) growth. Occurs in 𝛥𝑁 density-independent or very small populations. 𝛥𝑡 = 𝑟𝑁 S-shaped (limited) growth. Occurs in density-dependent populations as N approaches K. ∆𝑁 ∆𝑡 𝐾−𝑁 = 𝑟𝑁 ( 𝐾 ) Which of the following is not an important determinant of density-independent population size? a. Depletion of resources b. Natural disasters c. Poor competition d. Disease e. All of the above f. A and C g. A, C and D