Pre-Reading
advertisement

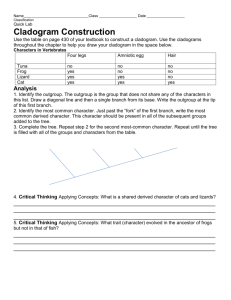
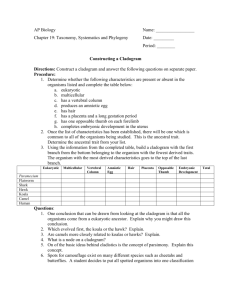
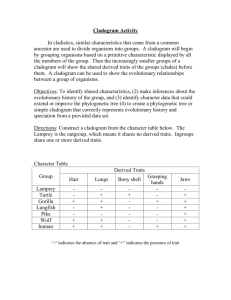
Comparing DNA Sequence to Understand Evolutionary Relationships with BLAST Name: _________________________________ Big Idea 1: Evolution Pre-Reading In order to understand the purposes and learning objectives of this investigation, you should begin by reading textbook Ch. 26 (pp. 536-548 only). Pre-Lab Activities Prior to attempting this investigation, prepare for the lab by working through the following online activities: 1. “The Evolution of Flight in Birds”, which can be found at http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/education/explorations/reslab/flight/main.htm. Complete the entire online activity – choosing “full speed ahead” when you come to the end of each section. 2. “What Did T-Rex Taste Like”, which can be found at http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/education/explorations/tours/Trex/. Complete the entire online activity. 3. “Journey into Phylogenetic Systematics”, which can be found at http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/clad/clad4.html. Read each section of material to strengthen your understanding of phylogeny and systematics. Pre-Lab Discussion Read the entire investigation. Then, answer the following questions. 1. Describe two reasons why being able to identify the precise location and sequence of human genes might be important. _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 2. What is bioinformatics? _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 3. What does bioinformatics allow us to accomplish quickly with genomes? _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 4. What is BLAST? What can it do? _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 5. What is a cladogram? _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 6. Review Figure 1. What does this cladogram suggest about the relatedness of Lycopodium, Selaginella, and Isoetes? _______________________________________________________________________________________ 7. What are shared derived characters? Why are these preferred over ancestral characters when building cladograms? _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 8. Review Figure 2. a. According to the cladogram, which organisms have lungs? _______________________________________________________________________________ b. According to the cladogram, what three structures do all lizards posses? _________________________________________________________________________________ c. According to the cladogram, which structure – dry skin or hair – evolved first? _________________________________________________________________________________ 9. Historically, only physical structures were used to create cladograms; however, modern-day cladistics relies heavily on genetic evidence. Why is genetic evidence preferred when constructing cladograms? What are the potential problems that may arise when using only physical characters? _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 10. Use the space below to draw a cladogram that depicts the evolutionary relationship among humans, chimpanzees, fruit flies, and mosses. After you complete your cladogram, explain what ancestral relationships exist among these four organisms. What characters did you use to classify these organisms and build your cladogram? Why did you choose these characters? The Investigations As you make your way through the investigations in this lab, record your responses to the lab questions in the spaces provided below. 1. Review Table 1. Use the data found in Table 1 and the space below to construct a cladogram of the major plant groups. 2. Review Table 2. a. Why is the percentage similarity in the gene always lower than the percentage similarity in the protein for each species? _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ b. Draw a cladogram depicting the evolutionary relationship among all five species (including humans) according to their percentage similarity in the GAPDH gene. Procedure Step 1 1. Review Figure 4. Form an initial hypothesis as to where you believe the fossil specimen should be placed on the cladogram based on the morphological observations you made earlier. Draw your hypothesis in the space provided below. Procedure Steps 2 – 4 1. Follow the procedures for downloading and analyzing data in BLAST exactly as they are described in the lab. Analyzing Results 1. What species in the BLAST result has the most similar gene sequence to the gene of interest? _______________________________________________________________________________________ 2. Where is that species located on your cladogram? _______________________________________________________________________________________ 3. How similar is that gene sequence? _______________________________________________________________________________________ 4. What species has the next most similar gene sequence to the gene of interest? _______________________________________________________________________________________ 5. Based on what you have learned from the sequence analysis and what you know from the structure, decide where the new fossil species belongs on the cladogram (Figure 4) with the other organisms. Redraw the cladogram you created before below – depicting the new placement of the fossil. 6. On the main page of BLAST, click on the link “List All Genomic Databases.” a. How many genomes are currently available for making comparisons using BLAST? _________ b. How does this limitation impact the proper analysis of the gene data used in this lab? _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ c. What other data could be collected from the fossil specimen to help properly identify its evolutionary history? _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________