Number System Fluency- Decimals
advertisement

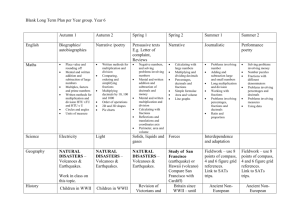
CCGPS Math 6 Unit 1 – Lesson 1 Unit Outline Title: Number System Fluency Name of Lesson: Decimal Operations Standards: Compute fluently with multi-digit numbers and find common factors and multiples. MCC6.NS.2 Fluently divide multi‐digit numbers using the standard algorithm. MCC6.NS.3 Fluently add, subtract, multiply, and divide multi‐digit decimals using the standard algorithm for each operation. Essential Question(s): Unit: How would I compute fluently with multi-digit numbers and find common factors and multiples? Lesson: When I divide one number by another number, do I always get a quotient smaller than my original number? What strategies are helpful when dividing multi-digit numbers? What strategies are helpful when performing operations on multi-digit decimals? What real-life situations require division? Assessment Description/Performance Task: Constructed response: Decimal Division Quiz Informal assessment: Justify Your Answer (Reason abstractly and quantitatively) Placemat Method (Make sense of problems and perseveres in solving them) Think-Ink-Write-Share (Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others) Performance task: Performance Task: Bargain Shopping Performance Task: Brain Only! Performance Task: Division Means Sharing Performance Task: How Are These Alike? Performance Task: Riding the Roller Coaster Performance Task: Sixth Grade Finds Out How Many Performance Task: Teacher for a Day Performance Task: What is 2,500 300? Performance Task: What’s My Rule? Performance Task: Division with Decimals Performance Task: Multiplication with Decimals Selected response: (TBD) Instructional Methods: Under the GPS curriculum, students in fourth grade were introduced to adding and subtracting decimals and dividing multi-digit whole numbers. This skill was further developed in fifth grade as students progressed to dividing with a multi-digit divisor and multiplying and dividing decimals (including decimals in the divisor and dividend). For the 2012-2013, this lesson should be review for students. However, students may not have been exposed to the vocabulary terms minuend and subtrahend. Opening: Hook/Activator: Make a 2 part flip book. Label one half Multiplication. Lead a discussion and generate all of the models of multiplication that have been discussed such as arrays, repeated addition, sets, number line model etc. Inside the multiplication half of the flip book, students should choose their favorite multiplication fact, write the equation, and solve it using repeated addition. Next, discuss which operation is the opposite (inverse) of multiplication. Students then CCSD Version Date: 2/16/2016 open the other half and label it Division. They should then write an equation related to the fact on the multiplication side. Since division is the inverse of multiplication, challenge students to use the inverse of repeated addition (repeated subtraction) to solve the division fact. Teaching Strategy: Set the stage by putting numbers into context: Display the following division problem on the board: 152 ÷ 25. Tell students the following: The school put up a sign to advertise a car wash in the school parking lot to raise money for library books. One hundred fifty two people signed up to have a car washed on Saturday. If one student can wash 25 cars in a day, how many students will have to work on Saturday in order to finish the job? Ask students to estimate how many cars they think each person washed and share with how they generated the estimate with their partner. Examples: 1. I estimate that each student washed about 5 cars because 25 is close to 30 and 152 is close to 150. I know that 150 ÷ 30 is 50 because 30 x 50 = 150. 2. I estimated that each student washed six cars because 25 is like a quarter and there are 6 quarters in $1.50. If students need a concrete approach to the problem, investigate the problem by using the base ten blocks to show 152 and break it into sets of 25s by making trades. Once this visual model of the problem is finished, show the repeated subtraction model of what happened when the students performed the task. (See picture below.) CCSD Version Date: 2/16/2016 Through class discussion, generate a written explanation of the division problem using repeated subtraction. (See EXAMPLE of the written explanation below. Note: Be sure that through whole class discourse, the students generate the written explanation. Therefore, explanations will vary.) Repeat the above steps if through informal assessment of the discussion and written piece, you CCSD Version Date: 2/16/2016 determine that your students need further modeling and in depth conversation about repeated subtraction as a strategy for solving a division problem. For the second half of the lesson, students will demonstrate their understating of decimal operations. To begin this topic, give each student a Place Value Chart and write numbers of your choice on the board. (Ex. 5.687, 9261.008, 14.29.) Ask students to turn to their neighbor and take turns reading the numbers as they are written. Remind students that they may use their “Hint” chart if they need assistance. Have students to create a foldable to review the steps and procedures for adding, subtracting, multiplying, and dividing decimals. View Study Jams interactive lesson on Double-Digit Division Use the Decimals and Fractions PowerPoint to enable students to see the relationship between division and decimals. SmartBoard Lesson on long division. Hands On Standards Grades 5-6 Resource: Lesson Add and Subtract Decimals & Lesson Multiply and Divide Decimals. Work Session: Students should use the work from the board as their example to solve the problem below. Each pair of students will need one sheet of chart paper and a marker. The chart paper should be folded in half. The first partner should solve the division problem using repeated subtraction on one half of the paper. The second partner should write the explanation of the problem on the other half of the paper. (Make base 10 blocks available to those who would like to build the problem.) Problem: Sharon’s soccer team won the tournament last weekend. Her mom brought chicken nuggets for the team’s celebration. There are 16 members of the team, and the restaurant put 137 nuggets on the tray. How many nuggets will each player get to eat? The following Learning Tasks may be used to build fluency with diving multi-digit numbers using the standard algorithm: Riding the Roller Coaster, How are These Alike?, Division Means Sharing, What is 2,500 300?, Sixth Grade Finds Out How Many. Use the Decimals Practice Exercise to reinforce ideas represented in foldable If students experience difficulty with multiplying and dividing decimals, use examples from the Modeling Decimals packet to review conceptual understanding. Assess students using the Decimal Division Quiz. The following Learning Tasks may be used to build fluency with decimal operations: Division with Decimals, Multiplication with Decimals, Brain Only, Teacher for a Day, What’s My Rule, Bargain Shopping. Closing: Summary by the Learner: Students will write their own division word problem, trade problems with a partner, and solve. Using the mnemonic S.T.O.P. On a notecard, students write: S - We STARTED the lesson by.... T - The TOPIC or (theme) today is.... O - Our OPPORTUNITIES to practice were..... P - The PURPOSE of learning this is..... Task Rotation – Students are given a story problem. Each member of the group completes a step in a different color using colored pencils. (As needed, the Q-Tips graphic organizer or other organizer may be used to assist students who have difficulty organizing information.) The first team to answer the question correctly will win a treat. A Picture Tells a 1000 Words – Show a picture of a solved problem. Have students to write a short statement and describe what they think the student did to solve the problem and what the student might have been thinking as he/she solved the problem. Human Paragraph – Have 5 students to stand in the front of the room. Students will pull from cards – Main Idea, Supporting Detail 1, 2, 3, Closing). Students will then review the various part of today’s lesson based on the part of the paragraph they choose.) Differentiation: (to be created) CCSD Version Date: 2/16/2016 Tiered Assignments: Leveled Questions: Multiple Intelligences: Using Realia/CRA: Choices Board: Open-Ended Tasks: Problem-Based Learning: Learning Contracts: Tiered Graphic Organizers: Other: Textbook/Online Resources: Holt Mathematics Course 1: Chapter 3, Lessons 3, 5, 6, and 7 Connected Math: Bits and Pieces III: Computing with Decimals and Percents Math in Context Hands-on Standards: Grades 5-6: Lesson Add and Subtract Decimals & Lesson Multiply and Divide Decimals http://www.learner.org/courses/learningmath/number/session9/part_a/area_division.html Vocabulary: difference dividend divisor minuend CCSD Version Date: 2/16/2016 product quotient subtrahend sum