Unit_Two-Estimation_and_Computation Objectives
advertisement

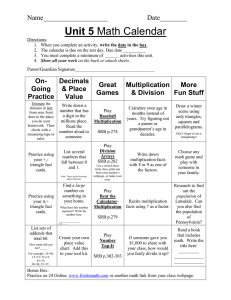
Unit Two-Estimation and Computation Content Objectives and Language Objectives Lesson 2.1 Content Objective: Students will devise an estimation strategy to solve a problem for which finding an exact answer is impossible. Language Objective: Students will discuss in partners how to make the best estimate and then defend it. Lesson 2.2 Content Objectives: Students will review place-value concepts for whole numbers and decimals, and will add using the partial-sums and column-addition methods. Language Objectives: Students will read about place values (p.29) and partial-sums & column-addition (p. 13)in the SRB, and students will write examples of the partial-sums and column-addition methods in their math journals. Lesson 2.3 Content Objective: Students will subtract multi-digit whole numbers and decimals by using the trade-first and partial-differences methods. Language Objectives: Students will read how to subtract using the trade-first (p. 15) and partial differences (p. 17) methods in the SRB as well as how to play the Top-It Game (p. 294). Lesson 2.4 Content Objective: Students will review a guide for solving number stories and concepts about number sentences. Language Objective: Students will use and write open sentences as aids in solving number stories. Vocabulary: variable Symbols (See next slide) 3+5=? Symbols Relation Symbols: < means less than > means is greater than =means is equal to Operation Symbols: + means plus - means minus x or * means times ÷ or / means divided by Lesson 2.5 Content Objective: Students will review statistical landmarks for sets of data and estimate reaction times. Language Objectives: Students will speak the Stand out Math chants for vocabulary, read about the “mean” in the SRB (p. 115), and use statistical landmarks to write and describe experimental data. Vocabulary: mean (or average), minimum, maximum, range, mode, median Lesson 2.6 Content Objective: Students will be introduced to the probability meter and estimate the probability of an event. Language Objectives: Students will listen, review, and apply vocabulary associated with chance events, and will review the Stand Out Math chant for “probability”. Lesson 2.7 Content Objective: Students will make magnitude estimates for products of multi-digit numbers including decimals. Language Objectives: Students will discuss in teams how to make magnitude estimate using multiplication and will read how to play multiplication Bull’s-eye in the SRB (p. 284). Lesson 2.8 Content Objectives: Students will use the partial- products method to multiply multi-digit whole numbers and will be introduced to products of decimals. Language Objective: Students will read about the partial-products method (p. 19) and the multiplication of decimals (p. 38) in the SRB. Lesson 2.9 Content Objective: Students will review and practice the lattice method for multiplication of whole numbers and decimals. Language Objectives: Students will discuss, listen, read, and write about the lattice method of multiplication in teams. Lesson 2.10 Content Objectives: Students will begin to understand the relative sizes of 1 million, 1 billion, and 1 trillion; and make an informed estimate from a sample of experimental data. Language Objective: Students will discuss the differences between a guess and an estimate, discuss what a “sample” is, and read about place values for whole numbers (p. 4 of SRB). Lesson 2.11 Content Objectives: Students will review and be assessed on the material covered in Unit 2. Language Objective: Students will write answers to review questions on dry erase boards as the class reviews.