CHAPTER 10 - FOUNDATION WALLS
advertisement

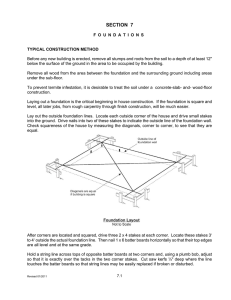
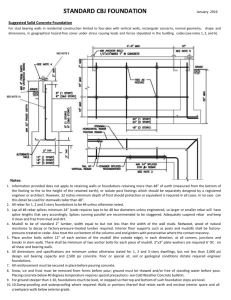
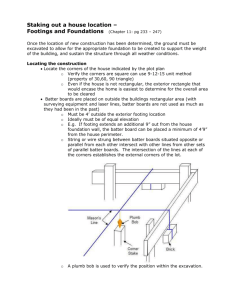
CHAPTER 10 - FOUNDATION WALLS 10.1 Footings Footing—is a base that provides a surface that distributes weight over a wide area of soil (generally made of concrete). Can be placed first before the foundation wall. Table 10-1 shows sizes of concrete or masonry footings in inches. Footing Design—Must be placed at least 12” below grade and far enough below finish grade to protect them from frost. Strength is greatly improved with reinforcing bar, or rebar. Other types of footings Pier footing—can be round or square, used to support girder floor systems. Stepped footing—used on a lot that slopes. 10.2 Concrete Foundation Walls 2 types of foundations walls: 1. full height foundation walls—tall enough for a full basement 2. crawl space foundation wall—shorter, usually 5 ft or less in height, common in mild climates, and reduces costs. Solid Foundation walls are usually 8- 10 inches thick. The foundation spreads the weight of the building over a greater area, thus the building does not settle. Superstructure—is all of the structure above the foundation. 10. 3 Concrete Block Walls Concrete block is popular for building foundation walls because they do not require formwork and they are fairly inexpensive. Concrete block walls can be strengthened with rebar. Good Mortar is essential for a strong solid wall. Anchor Bolts are placed at least 16 inches into the foundation wall to support (fasten) the preservative treated wood sill-plate.