Test answer key
advertisement

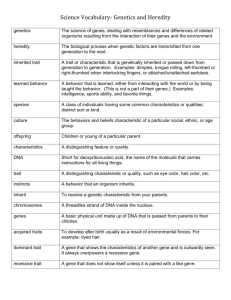
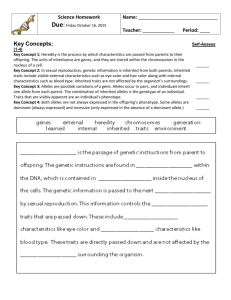
Test Fill in the blanks using words from the word bank: A. The Lysosome digests old DNA, protein, or lipids into small pieces, which can be used to make new molecules. B. The Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum carries lipids and proteins to the organelles or to the cell membranes; ribosomes are attached to the surface so they can be directly released for transport. C. The Mitochondria is the cell’s power plant because energy is made here as sugar molecules are digested. D. The Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum carries lipids and proteins to the organelles or to the cell membranes; contains enzymes that have specialized tasks, such as lipid synthesis. E. The Golgi Apparatus receives proteins and lipids from the Endoplasmic Reticulum. F. The Cytoplasm contains all of the organelles and a gel-like fluid that supports the organelles. G. The Nucleus contains all of the information the cell needs to do specific jobs, grow, and divide. H. The Cell Membrane gives the cell support and protects the cell from the outside environment; lets food and waste move in and out. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Mitochondria Cytoplasm Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Cell Membrane Lysosome Golgi Apparatus Nucleus Put these cell types in order as they occur during fertilization and growth: 2 A. Blastocyst Embryonic Stem Cells – when the embryo forms a hollow ball-like structure 5 B. Adult Stem Cells – cells reside in already developed tissue, direct growth through life 1 C. Early Embryonic Stem Cells – occurs when a newly fertilized egg begins to divide 3 D. Fetal Stem Cells – occurs during the 8th week of development, responsible for growth 4 E. Umbilical Cord Stem Cells – transports nutrient and oxygen-rich blood to the placenta Define the following words: Dominant Trait – A dominant trait is the trait that is visible regardless of the other traits. Recessive Trait – A recessive trait is a trait that can be masked or hidden by the dominant trait. Gene – A gene is the part of DNA that contains the heredity information from your family. Answer the following questions: Can a baby’s eye color be predicted by their relatives? Yes, using the parents, grandparents, and great-grandparents traits, it can be predicted which traits the baby will have visible. If you have 2 of each gene, where did these two genes come from? One comes from your mother and one from your father. How many gene pairs determine eye color? There are actually three gene pairs that determine eye color. Define the following words: Punnet Square – A probability tool used to look at dominant and recessive traits Homozygous – When a person has two alike traits in a gene pair, ex: BB or bb Heterozygous – When a person has two different traits in a gene pair, ex: Bb Complete the following Punnet Squares: Eyes D d D DD Dd D DD Dd Phenotypic Ratio: 4:0 Ears E e E EE Ee e Ee ee Phenotypic Ratio: 3:1 Freckles f f F Ff Ff f ff ff Phenotypic Ratio: 2:2 Tongue t t T Tt Tt T Tt Tt Phenotypic Ratio: 4:0 Match the genes with their partners. Write how many hydrogen bonds occur between each pair: Cytosine – pairs with Guanine – there are three hydrogen bonds between these two Thymine – pairs with Adenine – there are two hydrogen bonds between these two Adenine – pairs with Thymine – there are two hydrogen bonds between these two Guanine – pairs with Cytosine – there are three hydrogen bonds between these two Define the following vocabulary words: DNA – any of various nucleic acids that are usually the molecular basis of heredity, are localized especially in cell nuclei, and are constructed of a double helix held together by hydrogen bonds Double helix – a helix or spiral consisting of two strands in the surface of a cylinder that coils around its axis; especially the structural arrangement of DNA Nucleotide – any of several compounds that consist of a ribose or deoxyribose sugar joined to a purine or pyrimidine base and to a phosphate group and that are the basic structural unit of nucleic acids (as RNA and DNA) Answer the following question: What does DNA look like? DNA is a structure that looks similar to a ladder. There are stabilizers on the outside of the ladder running up and down the structure. The rungs are the gene pairs connected by hydrogen bonds. This ladder is twisted into a double helix structure; it coils around the center.