CHAPTER 3 HEREDITY AND GENETICS
advertisement

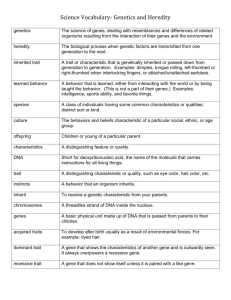
CHAPTER 5 HEREDITY AND GENETICS What is heredity? OBJECTIVE: Explain why offspring have some of the traits of their parents but not all. Key Terms trait: characteristic inherited (ihn-HEHR-ih-tuhd) trait: trait that are passed from parents to their offspring heredity (huh-REHD-ih-tee): passing of traits from parents to offspring genetics (juh-NEHT-ihks): study of heredity Lesson Summary • Traits are the characteristics of an organism. • The passing of traits from parents to offspring is called heredity. • The field of biology that studies heredity is called genetics. Key Terms sperm cell: male reproductive cell egg cell: female reproductive cell gamete (GAM-eet): reproductive cell Lesson Summary • Every body cell of an animal contains the same number of chromosomes. • Sperm cells and egg cells are gametes, or reproductive cells. Gametes contain half the number of chromosomes of a body cell. • Gametes from through a process called meiosis. What is DNA? OBJECTIVES: Describe the molecular makeup of DNA. Explain the role of DNA in living organisms. Key Terms DNA: large molecule contained in chromosomes replication (rehp-lih-KAY-shuhn): process by which DNA is duplicated protein synthesis: process by which proteins are made Lesson Summary • Chromosomes are made of large molecules called DNA. • DNA contains sugars, phosphates, and four nitrogen bases: adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine. • The structure of DNA was discovered by James Watson and Francis Crick, with the help of other scientists. • Before mitosis can occur, DNA molecules make copies of themselves during replication. This results in two identical DNA strands. • DNA contains a genetic code that determines the kinds of inherited traits an organism will have. • Proteins are produced during a process called protein synthesis. RNA is a molecule involved in protein synthesis. What are chromosomes? OBJECTIVE: Describe how genes and chromosomes are involved in heredity. Key Terms genes (JEENZ): parts of a chromosome that control inherited traits allele (uh-LEEL): one of two or more forms of a particular gene Lesson Summary • • • • Chromosomes are made up of chromatin. Chromatin is composed of long, thin strands of DNA. Genes control inherited traits such as eye color and hair color. . Organisms that carry out sexual reproduction have chromosomes that exist in pairs. Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes. • Alleles are different versions of the same gene. For example, the gene for hair color may have one allele for brown hair and one for black hair. Why can offspring differ from their parents? OBJECTIVE: Explain the difference between dominant and recessive traits. Key Terms homozygous (hoh-moh-ZY-guhs): having two like genes for the same trait heterozygous (heht-uhr-oh-ZY-guhs): having two unlike genes for the same trait dominant gene: gene whose trait always shows itself recessive gene: gene of a trait that is hidden when the dominant gene is present Lesson Summary • • • • • Each trait of an organism is determined by at least one gene from each parent. Organisms that are homozygous have two like genes for a specific trait. Organisms that are heterozygous have two unlike genes for a specific trait. In heterozygous organisms, the trait of the dominant gene is always expressed. The recessive gene’s trait does not show itself in the organism. 3-6 How do genes combine in offspring? OBJECTIVE: Identify what causes differences in the traits of parents and their offspring. Key Term Punnett square: chart that shows possible gene combinations Lesson Summary • In organisms with at least two genes for each trait, each parent contributes one of the genes. • Letters are used to represent genes when written. Uppercase letters represent dominant genes. Lowercase letters represent recessive genes. • Punnett squares are charts used to show the possible combinations a set of genes may exhibit. • If one parent is homozygous dominant and the other parent is homozygous recessive, all offspring will be heterozygous dominant. • If both parents are heterozygous for a trait, the offspring have a 25% chance of being homozygous dominant, a 50% chance of being heterozygous dominant, and a 25% chance of being homozygous recessive.