Approach - Serwis Informacyjny WSJO
advertisement

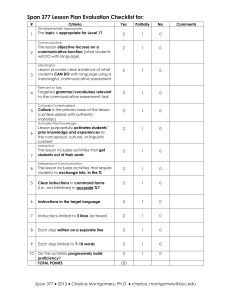
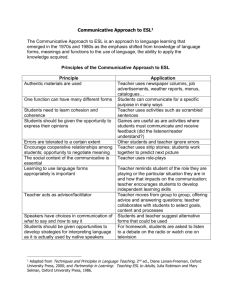
Approach Founder if Any known. Main Idea What is taught Grammar translation Structural approach J.B. Watson (1942 Cognitive approach Noam Chomsky Communicative approach Audiolingualism Application of methods used in Latin and Greek to teaching of modern languages. Rules of grammar, not the language itself, are all important. Verb declensions are set out tables, vocabulary lists to be learned, leading to translation from mother tongue into target language and viceversa. Little or no attention to pronunciation. Assumption was that language consists of written words and of words which exist in isolation, as though they were individual bricks which could be translated one by one into their STRUCTURES ! “language was like a game of chess, a system in which each item is defined by its relationship to all the others…language is a carefully built structure of interwoven elements.”( CREATIVITY “..the ability of human beings to produce and comprehend an infinite number of novel sentences.” Communicative Language Teaching (CLT) is an approach to the teaching of secondandforeig language that emphasizes ineractionas both the means and the ultimate goal of learning alanguage. It is also referred to as “communicative approach to the teaching of foreign languages” or simply the “Communicative Approach” It is based on behaviorist theory, which professes that certain traits of living things, and in this case humans could be trained through a system of reinforcement—correct use of a trait would receive positive feedback whileincorrect use of that trait would receive negative feedback. Structures, The structuralists, whose views are related to behavioral psychology, see language as a finite list of ordered elements to which one can attach labels. They undertake a systematic analysis of structure. The teacher depends on such structural description as the distribution and combination of elements into a chain of speech. It is based on They look for a universal grammar that contains universals relating to the deep-seated regularities characterizing all languages. For instance, subject and predicate, negative and adjectival forms are present in all languages because they are a universal feature, whereas the structuring and , CLT also places great emphasis on helping students use thetarget language in a variety of contexts and places great emphasis on learning languagefunctions. ALM, its primary focus is on helping learners create meaning rather than helping them develop perfectly grammatical structures or acquire native-like pronunciation. This means that successfully learning a foreign language is assessed in termsof how well learners have developed their communicative competence, which can loosely bedefined as their foreign equivalents and then assessed according to grammatical rules into sentences in the foreign language. How it is taught Through a translation done by students of a source into a foreign language or from a foreing language into the students first language. the process of substitution, the replacement of one unit by another unit of the same grammatical class. arrangement of these features belong to individual languages. The deep structure rules are limited by the grammar of each particular language. Universal grammar, according to Chomsky is “…a theory of the “initial state” of the language faculty, prior to any linguistic experience.” Mimicry and imitation To the cognitivist, and memorisation, there children are born with is no distinction an innate capacity for between the first and language second language development. The teaching. There is no human brain is internal process. “ready” for language, Stimulus and in the sense that when reinforcement (or children are exposed reward) from the input to speech, certain and the “verbal operant” general principles for (or response) forms the discovering or output. structuring language automatically begin to operate, there exists a LAD within children. LANGUAGE AQUSITION DEVICE ability to apply knowledge of both formal and sociolinguistic aspects of alanguage with adequate proficiency to communicate. The main objective of CLT is to develop the communicative competence of the learners.ii) Learners are involved in the learning process so that language developsautomatically.All the basic four skills get equal emphasis. The development of oral proficiency in the language through carefully selectedvocabularies which form a general service list for the learner to use.ii)To make students able to use the target language communicatively andautomatically without stopping to think.Communicative Language Teaching:i)The main objective of CLT is to develop the communicative competence of the learners.ii) Learners are involved in the learning process so that language developsautomatically.All the basic four skills get equal emphasis. Main ideas summary This method gives pupils the wrong idea of what language is and of the relationship between languages. Language is seen as a collection or words which are isolated and independent and there must be a corresponding word in the native tongue Speech is primary, writing secondary, so the habits that are formed in language must be speech habits. Automatic response is best achieved by constant repetition. Offshoots of this theory are the language laboratory, structural drill, imitation, and memorization techniques.( can provide much useful information concerning verbal responses and reinforcement Low translation standard - caused by grammatical tends to manipulate techniques which the language and force learner to disregard the content. deduce FL sentences 'by selecting from a multiplicity of rules and exceptions and individualised words. Speech is primary, writing secondary, but also important so the habits that are formed in language must be speech habits. provides much useful information on the basic nature of the organism and its internal processes makes little or no account of stimulusresponsereinforcement Language as it is used in real context should be introduced Fluency is much more important than accuracy The teacher acts as an advisor during communicative activity, a facilitator of students’ learning, a manager of classroom activity, or a co-communicator Students should be given opportunities to develop strategies for interpretinglanguage as it is actually seen by native speakers Students are communicators and are actively engaged in negotiating meaning. Language is used a great deal through communicative activities such as games,role-play, problem solving Language is speech and not writing Language is a set of habit. Learning is controlled through behaviour Language forms occur within a context Teaching is directed to provide students with a nativespeaker-like model Errors are carefully avoided because they lead to the formation of bad habits Positive reinforcement helps the student to develop correct habits. Language is not seen separated from culture. Culture is the everyday behavior of people who use the target language EX 1. 1. This new service will be available to all users _______ up for paid membership. A. that signed B. that signed it C. which signed D. sign 2. John Smith, _______ of economic crimes, tax evasion and fraud, is being accused of attempted murder now. A. of that he was accused B. that was accused C. whom he was accused D. who was accused 3. The police were greatly outnumbered by rioters, _______ ran into the hundreds. A. whose figures B. those figures C. that its figures D. its figures that EX 2. Translate the followin text into Polish. "Show me a man or a woman alone and I'll show you a saint. Give me two and they'll fall in love. Give me three and they'll invent the charming thing we call 'society'. Give me four and they'll build a pyramid. Give me five and they'll make one an outcast. Give me six and they'll reinvent prejudice. Give me seven and in seven years they'll reinvent warfare. Man may have been made in the image of God, but human society was made in the image of His opposite number, and is always trying to get back home." EX 3. Put the verbs into the correct tense (simple past or past progressive) and explain their usage. 1. When I (do) w as doing 2. While Tom (play) broke the piano, his mother (do) 3. He (drink) 4. I (have) the washing-up, I (break) a plate. the washing-up. some juice and then he (eat) a few chips. dinner when I suddenly (hear) a loud bang. 5. When my father (work) in the garden, an old friend (pass) by to see him. Put the verbs into the correct tense (simple past or past progressive). 1. When I (do) w as doing 2. While Tom (play) broke the piano, his mother (do) 3. He (drink) 4. I (have) the washing-up, I (break) a plate. the washing-up. some juice and then he (eat) a few chips. dinner when I suddenly (hear) a loud bang. 5. When my father (work) in the garden, an old friend (pass) by to see him. EX 4. The teacher names a few thing around him/her for example (a chair, a table, a window, a door) Then the teacher asks questions about the things pointing at them: What is this? This is a …. (a chair, a table, a window, a door) What colour is this (a chair, a table, a window, a door)? It … And so on… EX 5. “Teacher: There's a cup on the table ... repeat Students: There's a cup on the table Teacher: Spoon Students: There's a spoon on the table Teacher: Book Students: There's a book on the table Teacher: On the chair Students: There's a book on the chair