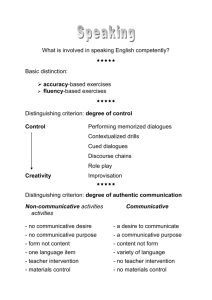
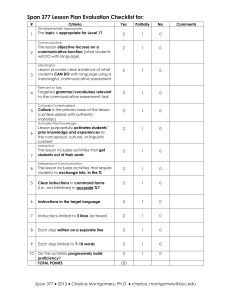
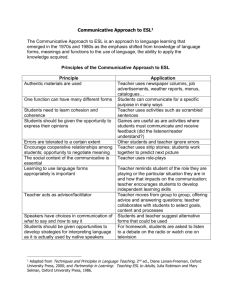
1. What, why and how do we write?
advertisement

Unit 12 Teaching Writing Teaching objectives know how to motive students to write design writing tasks A communicative approach and a process approach to writing Teaching contents What, why and how do we write? A communicative approach to writing Problems in writing tasks A process approach to writing Motivating students to write Designing writing tasks Using the Internet to promote process of writing 1. What, why and how do we write? There is a great variety of things we write in reality, e.g., letters, journals, notes,, instruction, posters, essays, reports, menus. We write for various reasons, such as to convey messages or just to keep a record of what is in our mind. Writing can be less threatening for anxious students and can raise awareness of how language works. As to the way we write, writing can be both collaborative and solitary. 2. A communicative approach to writing To motivate students, it is necessary to engage them in some act of communication. This means either writing for a specific recipient, or engaging in an act of creative writing where their work is intended to be read by other people, in other words, an intended audience be motivated by authentic writing tasks that have some communicative elements. 3. Problems in writing tasks 1. They are mainly accuracy-based. 2. They are designed to practice certain target structure 3. There is insufficient preparation before the writing stage. 4. There is no sense of audience. 5. There is no sense of authenticity. 6. Students are given ideas to express rather than being invited to invent their own. 7. There is no opportunity for creative writing, particularly for expressing unusual or original ideas. 4. A process approach to writing The product-oriented method of teaching writing pays great attention to the accuracy of the final product but ignores the process, which the students go through to reach the final goal. What really matters or makes a difference is the help that the teacher provides to guide the students through the process that they undergo when they are writing. This is called the process approach to writing. 4.1 Features of process writing Focus on the process of writing that leads to the final written product Help student writers to understand their own composing process; Help them to build repertoires of strategies for prewriting, drafting, and rewriting; Give students time to write and rewrite; Place central importance on the process of revision; Let students discover what they want to say as they write; Give students feedback throughout the composing process (not just on the final product) to consider as they attempt to bring their expression closer and closer to intention; Encourage feedback both from the instructor and peers; Include individual conferences between teacher and student during the process of composition. 4.2 Procedures of process writing Creating a motivation to write Brainstorming Mapping Free writing Outlining Drafting Editing Revising Proofreading Conferencing 5 Motivating students to write Make the topic of writing as close as possible to students’ life. Leave students enough room for creativity and imagination. Prepare students well before writing. Encourage collaborative group writing as well as individual writing Provide opportunities for students to share their writings. Provide constructive and positive feedback. Treat students’ errors strategically. Give students a sense of achievement from time to time. 6. Writing through e-mail E-mail provides a perfect mechanism for students to submit drafts and for teachers to look them over at their convenience and send them back with comments. New ideas are shared promptly and can be responded to quickly. Another advantage is that the teacher can easily store all the drafts of a document for later review and analysis of the revision process. The end!