Testing
advertisement
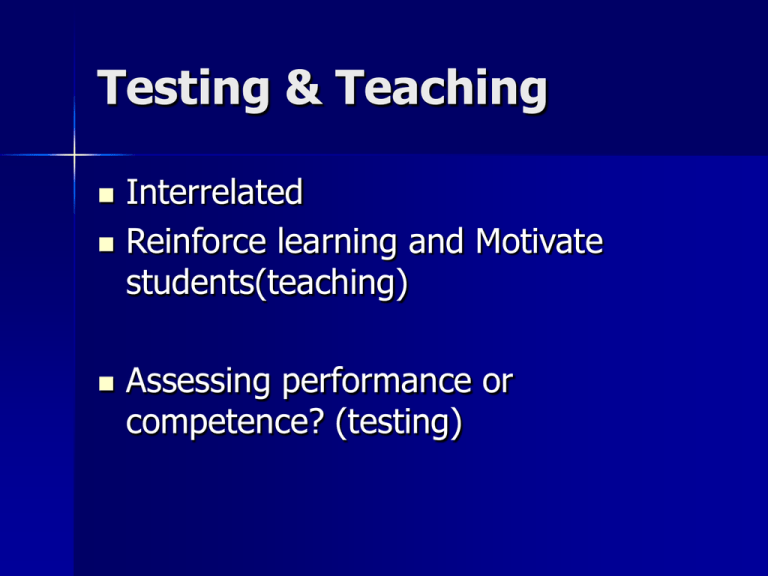
Testing & Teaching Interrelated Reinforce learning and Motivate students(teaching) Assessing performance or competence? (testing) Effects of a test A language test: Which type of assessment is powerful? – (a)everyday communication – (b)Mechanical test of structure Negative effects Mechanical Tests – Grammar tests – Translations? – Language manipulation Positive effect Communicative Test – Improved learning habits – Motivation (to show their ability to perform certain tasks, learning from their weakness through feedback) – Use language in authentic milieu Public Exams/Standardized Tests Public Exams May attempt to measure success in communication through performing purposeful tasks Beneficial influence on syllabuses and teaching strategies non-beneficial: if it is instrumental: YDS? Measuring each performance in comparison with other students Or with a certain established forms Why test? Function: – Comparison – Selection – Practising teacher Indivudual Evaluation: (1)Classroom vs (2)External (1)Clasroom Test(for making adjustment in teachers teaching strategies, classifying) : administrative exams; quiz, visa, final, midterm (2)External Test (for selection): ÖSS, LGS Outcomes of the tests External Test: selection! Class Test: evaluation of the effectiveness of their teaching – To locate precise areas of difficulty encountered by the class or individuals – Diagnosing weakness and difficulties (doctor) – First identify errors then assist them – first find difficulties of the programme then judge syllabus – As well as methods and materials – Pedagogical: – Test Result } Certain unsufficient areas of syllabus for FLL} planning remadial or further teaching (7 or six students out of in a class of 30 or 40) What should be tested and to what standard? Language is a complex phenomenon Decriptive and prescriptive approaches? – includes linguistic elements and nonlinguistic elements (gestures, eyemovements) – Communication requires all these units Standards for testing Mistakes for L1 and L2 users Capacity of L2 learners Testing the Language Skills * Communicative Skills (integrated areas) – Listening – Listening and speaking – Reading and writing Test items must comprise use of language in real-life communication=oral interaction (authentic milieu) √ questioning the ability to understand and respond appropriately to polite requests, advice, etc X reading aloud or telling stories Testing writing Do not require students write compositions But, require students to write letters, memos, reports and messages Testing Reading & Listening Write questions which extract your students creative look; specific information of a practical nature! But do not prefer to write questions testing unimportant specific details! Traditional Reading tests:answering techniques But not: ability to read or sense and scan to extract specific informations, general fluency, ability to tandle TL Ways of assessing four major skills Do not consider that your purpose can best be achieved if each separate skill can be measured on it is own. Because, separating each skill is difficult in terms of communication. Testing Language areas Testing isolated language areas – Grammar and usage – Vocabulary (meaning, word formatios, collocations) – Phonology (phonemes, stress, intonation) Test of Grammar & Usage M.C / item ITEM: interrogative form or statement M.C.: only one answer is normally correct for each item Test of Vocabulary Measuring knowledge about meaning of certain words, paterns, colocations Active vs passive skills ACTIVE Vocabulary: performance in speaking and writing PASSIVE Vocabulary: competence; recognizing while listening and reading SAMPLING: to select VOCABULARY items A Multiple choice mechanic teast Tests of Phonology Sub-skills: – Ability to recognise and pronounce the significant sound contrasts of a language – Ability to recognise and use the stress patterns of a language – Ability to hear and produce the melody or patterns of the tunes of a language(the rise and fall of the voice The following test does not indicate an ability to speak. It is just a phonem-discrimination at low level. And not communicative Language Skills and Language Element Testing students’ ability to handle elements of language correctly? Testing integrated skills? – Level and purpose of the test – if proficiency(level) is low then test elements – if purpose is sampling a field: use battery tests=assessing mastery of of language elements. At all levels but not elementary: include test items measuring the ability to communicate in L2 Not important: testing phonemes such as /i:/ or /I/: Look at that sheep sailing slowly out of the harbour – Contextual clue, redundancy Best Test: Successful communicative test in real life (performance) – Thus, fluency in English can be judged: ability to express facts, ideas, understand what heard and read – Oral interviews and letter-writing assess performance in those skills used in real life. – P.10 see