CHANGING STATES OF MATTER
advertisement
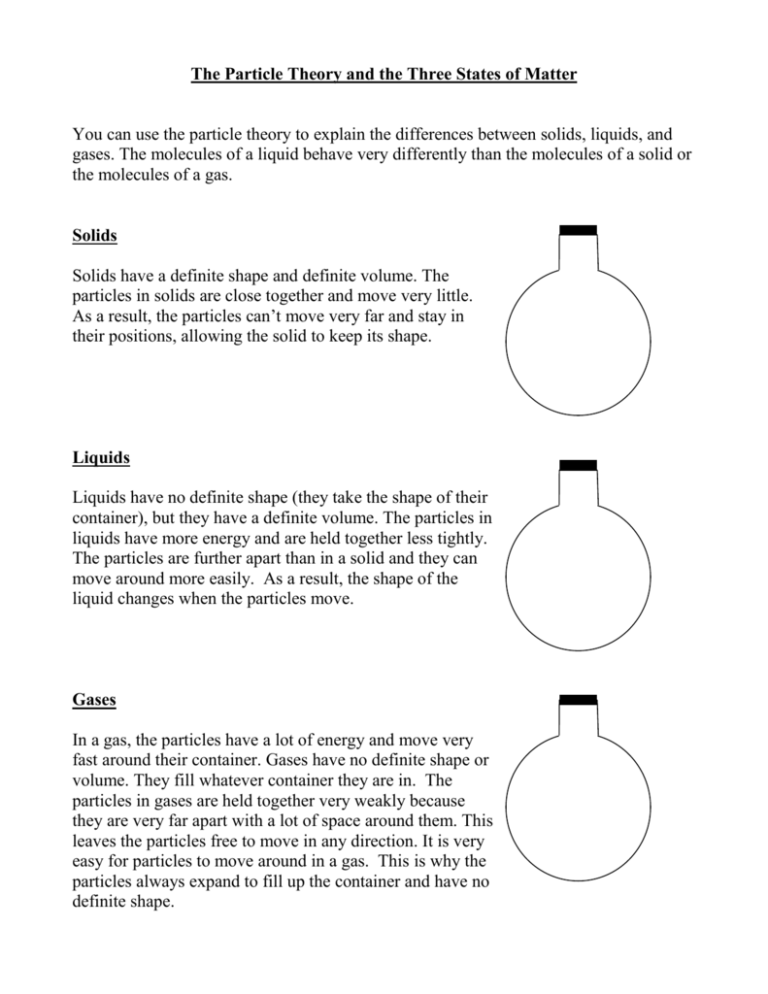
The Particle Theory and the Three States of Matter You can use the particle theory to explain the differences between solids, liquids, and gases. The molecules of a liquid behave very differently than the molecules of a solid or the molecules of a gas. Solids Solids have a definite shape and definite volume. The particles in solids are close together and move very little. As a result, the particles can’t move very far and stay in their positions, allowing the solid to keep its shape. Liquids Liquids have no definite shape (they take the shape of their container), but they have a definite volume. The particles in liquids have more energy and are held together less tightly. The particles are further apart than in a solid and they can move around more easily. As a result, the shape of the liquid changes when the particles move. Gases In a gas, the particles have a lot of energy and move very fast around their container. Gases have no definite shape or volume. They fill whatever container they are in. The particles in gases are held together very weakly because they are very far apart with a lot of space around them. This leaves the particles free to move in any direction. It is very easy for particles to move around in a gas. This is why the particles always expand to fill up the container and have no definite shape. CHANGING STATES OF MATTER The changes in the states of matter are really the changes in the way molecules move. When a liquid is heated, its molecules change the heat energy to moving energy. The liquid molecules begin to move faster and move further apart from each other. Molecules near the surface of a hot liquid jump up into the air and become a part of the air as a gas or vapour. When a liquid is cooled, its molecules lose moving energy. The liquid molecules move slower and move closer together. As the molecules of liquid slow down, they become a solid. Changing States of Matter Questions 1. What happens to molecules when they are heated? 2. What happens to molecules when they are cooled? 3. When molecules move faster, they move (farther apart, closer together). FREEZING: A change from Liquid to Solid Freezing turns a liquid into a solid when the temperature of the liquid is lowered to a certain point. As a substance freezes, its molecules move slower and they move closer together. The temperature at which a substance freezes is called its freezing point. Every substance has its own freezing point. Alcohol freezes at about -94 C. Will alcohol freeze if the temperature is –35 C outside?_________ Water freezes at 0 C. Will water freeze if the temperature outside is –35 C?_______ Why do we need to know the freezing points of different substances? Freezing points are very useful, especially in a cold country like Canada. In the winter, we need ways to keep water from freezing. In cars, the radiator is filled with water. If this water were allowed to freeze it would cause the radiator to crack. By mixing water and alcohol, we can lower the freezing point of the liquid we put in the radiator. This prevents the liquid from freezing when it gets cold outside. When most substances freeze, they contract or get smaller. This is because the molecules in a frozen substance move very little and stay very close together. Water, however, expands when it freezes. Its molecules are arranged in a definite pattern with big spaces between them. These spaces make ice take up more space, or expand. Below-freezing temperatures can freeze water pipes in cold basements. The water expands as it freezes, cracking the pipes. When the temperature rises, the ice melts to water and the basement is flooded. Freezing Questions 1. Freezing is when a ______________ turns into a ______________. 2. What is the freezing point of a liquid? 3. Water (expands, contracts) when it freezes. 4. Most substances (expand, contract) when they freeze. 5. Why do pipes that are full of water break when it is cold out? 6. Freezing occurs when heat is (added, removed). MELTING: A change from a Solid to a Liquid Melting turns a solid into a liquid. Heat must be added for a substance to melt. The temperature at which a solid melts is called its melting point. When a substance melts, its molecules move faster and faster and move further apart to form a liquid. Silver, gold, and iron have very high melting points. We must add heat to them before they will melt. The melting point of ice is 0 C. Dry ice melts to the gas carbon dioxide. Dry ice is formed when carbon dioxide gas is put under pressure, forced into metal cans, and cooled to form liquid carbon dioxide. The liquid carbon dioxide is then frozen to form DRY ICE. Dry ice is so cold, it will burn your hands. Never touch dry ice! When dry ice melts, it goes directly from a solid state to a gas state. Dry ice does not melt to a liquid state. Melting from a solid to a gas is called SUBLIMATION. Dry ice is used to ship seafood and meat, because it keeps the food frozen, but doesn’t ruin the packing box and paper. Why not? Melting Questions: 1. Melting is when a __________turns into a __________. 2. What is the melting point of a substance? 3. The opposite of melting something is ______________something. 4. When a solid turns directly into a gas, we call it _____________________. 5. What is solid carbon dioxide called? 6. Melting occurs when heat is (added, removed). CONDENSATION: A change from a Gas to a Liquid When a gas is cooled, the loss of heat causes the gas to condense into liquid. This is called condensation. The molecules of gas slow down and move closer together to form a liquid. An example of condensation is when warm air is cooled by contact with a cold surface and water droplets form. The liquid droplets on the surface are called condensation. Blow your warm breath on a cold windowpane or mirror. The warm air you exhale (breathe out) will condense on the cool surface. Condensation is the opposite of EVAPORATION. EVAPORATION: A change from a liquid into a gas Evaporation changes a liquid to a gas when heat is added. As the liquid heats up, the molecules begin to move faster and further apart, causing molecules on the surface of the liquid to rise into the air. We say that the liquid vaporizes into a gas. Condensation and Evaporation Questions 1. Condensation is when a ______________ turns into a __________________. 2. Condensation occurs when heat is (added, removed). 3. Condensation is the opposite of ____________________. 4. Evaporation is when a ______________ turns into a __________________. 5. Evaporation occurs when heat is (added, removed). 6. Put C under the pictures that show condensation. Put E under the pictures that show evaporation. The States of Matter Matter can exist in 3 states: solid, liquid, or gas. The state of matter is one of its physical properties. The table below describes the states of matter in terms of shape and volume. State Solid Shape Liquid Gas For each state of matter, find 4 examples: Solid: Liquid: Gas: Volume