Vascular Seed Plants
advertisement

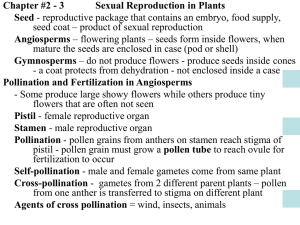
Vascular Seed Plants • 2 major groups are: • Name the 2 major vessels and their function: 1. 2. • Name the 3 major vascular organs and describe their functions: 1. 2. 3. • What is a seed? –Angiosperms: seeds are stored in ___________________ –Gymnosperms: seeds are stored in _________________ GYMNOSPERMS • Literally means: •Examples: •No ____________, seeds in ______________ •Leaves are ________________ •Evergreens = ________________________________________ •Uses: Gymnosperm Reproduction •Sporophyte tree contains _____________________________ •Primary pollinator = ______________ Male Cone (list 4 characteristics) 1. 2. 3. 4. Female Cone (list 5 characteristics) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Steps of Reproduction •Pollen grain is carried by __________ from __________ cone to _________ cone •Pollen grain ___________ to female cone •Pollen grain grows ________________ down to the _________ •_____________ swim down pollen tube to the eggs •__________________ •____________ develops inside a __________ •Female cone ____________ up and _____________ seeds (during the __________ & ___________) •During the ___________ new trees will grow Angiosperms •2 classes: •Reproductive organ is the ___________________ •Stores seeds in _______________________ •Uses: (list 5 uses) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Angiosperm Reproduction •_____________________________________ carry pollen grain to the ____________ •Pollen grain _____________ to the stigma & grows a _______________ •____________ swim down the pollen tube to the __________ where the _________ are •Fertilization •____________ develops inside the __________ •Ovary continues to grow _____________________ •____________ parts fall off and ripened ovary (____________) remains on the plant Fruits & Seed Dispersal •Ripened ovary (fruit) ______________ the developing seeds and becomes the ______________________________ for the growing seed •Attracts _________________ to eat it so that they can _______________ the seeds •Seed dispersal: (list 4 things that can disperse seeds) 1. 2. 3. 4. Roots •2 types: (List the 2) 1. 2. List 2 examples of TAP roots 1. 2. Stems •2 Types: (list the 2) 1. 2. List 3 examples of specialized stems that are enlarged and contain sugar 1. 2. 3. Leaves •Absorb _________________ for __________________ •Absorb ______________ thru __________________ •Contain the most _________________ & chlorophyll Tropism: _________________ in response to _________________ •Phototropism: _____________ (stems, branches, leaves) •Hydrotropism: ____________ (roots) •Gravitropism: _____________ (all parts) –Positive = grows _____________ gravity –Negative = grows ______________ gravity