SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF RESPIRATORY DISEASES
advertisement

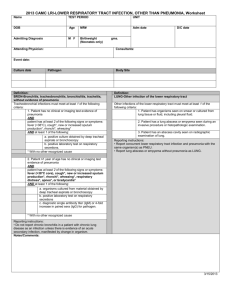
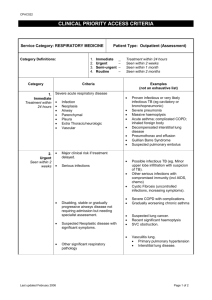
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF RESPIRATORY DISEASES LEARNING OBJECTIVES: By the end of this session, students should be able to: Enumerate the various symptoms of respiratory disorders. Enumerate the different signs ellicitied after a clinical examination of a patient with respiratory disorders. Correlate the symptoms with the signs of respiratory distress. Determine the cause of respiratory distress in a patient with particular sign or symptom SYMPTOM: • Patient’s subjective assessment of disease or physical disturbance • Problems the patient complains about or seeks relief from. SIGN: • Objective evidence of the presence of a disease or disorder, as elicited by the doctor Symptoms • • • • • • • • Cough Breathlessness / dysnea Chest pain Hemoptysis Syncope Palpitations Weight loss Fatigue SIGNS • • • • • • • • • • Tachypnea Tachycardia Cachexia Wheezing Sputum Use of accessory muscles of respiration Decreased chest expansion Vocal Resonance Decreased breath sounds crepitations COUGH • To expel air suddenly and noisily from the lungs through the glottis, either as the result of an involuntary muscular spasm in the throat or to clear the air passages Causes: • Asthma • Allergies • COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease) • GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease) • Smoking • Throat disorders, such as croup in young children • Some medicines SPUTUM Sputum is matter that is expectorated from the respiratory tract, such as mucus or phlegm, mixed with saliva Types and causes: – Serous e.g., Pulmonary edema – Mucous e.g., chronic bronchitis, COPD, asthma – Mucopurulent (brown, yellow, green) e.g., Infection – Rusty e.g., pneumococcal pneumonia BREATHLESSNESS Shortness of breath; difficult or labored breathing. Associated sign: Tachypnea (increased respiratory rate) o Normal: 12/min Causes: increased ventilatory drive and decreased ventilatory capacity Dyspnea with CVS patholgy: Ischemic heart Disease Dyspnea with Respiratory pathology: Asthma COPD Emphysema Infections (pneumonia and T.B.) Hypoxia Acidosis/ metablic disorders Disorder Acute cause Chronic cause Association of dyspnea of dyspnea with exercise Asthma Acute on chronic yes Increased (exercise induced) COPD No Yes Increased Emphysema Maybe Yes Increased Lung Infections Yes Yes (T.B.) (pneumonia) Increased Hypoxia Yes Yes (COPD) Increased Acidosis Yes Yes Increased CHEST PAIN Chest pain is a manifestation of a number of serious conditions and is generally considered a medical emergency. • Associated sign: – Tenderness on palpation (bone or muscular pathology) – Decreased chest expansion (respiratory or cardiovascular pathology) CAUSES: CENTRAL: CVS pathology, e.g, IHD • PERIPHERAL: Respiratory pathology e.g., • Pneumothorax • pulmonary embolism • Pleurisy • lung cancer HEMOPTYSIS • Spitting or coughing up blood or bloodystained sputum Causes: • T.B. • Lung carcinoma • Pneumonia SYNCOPE • Temporary loss of consciousness due to generalized cerebral ischemia Causes: • Pulmonary embolism • Emphysema • Internal bleeding • High grade fever • Vasovagal shock PALPITATIONS and TACHYCARDIA • TACHYCARDIA: A rapid heart rate, usually defined as greater than 100 beats per minute. • PALPITATIONS: A sensation in which a person is aware of an irregular, hard, or rapid heartbeat. WEIGHT LOSS • A reduction in body mass characterized by a loss of adipose tissue (body fat) and skeletal muscle • Associated sign: – Cachexia Causes: • T.B. • Lung carcinoma • Chronic diseases e.g., COPD, asthma etc FATIGUE Fatigue is physical and/or mental exhaustion that can be triggered by stress, medication, overwork, or mental and physical illness or disease. CAUSES: • Infection • Inflammation • Trauma • malignancy • chronic disease e.g., COPD • autoimmune diseases TRACHEAL DEVIATION Towards the side of lesion: • Lung collapse (with or without pneumothorax on opposite side) • Fibrosis e.g., in bronhiectasis or cavitation Away from the side of lesion: • Space occupying lesion • Fluid in the space: plueral effusion or empyema • Air in the space: pneumothorax USE OF ACCESSORY MUSCLES OF RESPIRATION ACCESSORY MUSCLES OF RESPIRATION: • Scalene muscles • Sternocleidomastoid • Trapezius • Serratius anterior • Pectoralis major and minor • Latissimus dorsi Causes: • COPD • Decreased vital capacity (Emphysema) • Spinal cord injury (cervical) DECREASED CHEST EXPANSION • • • • • • • Consolidation Lung collapse Fibrosis Cavitation Pleural effusion Empyema pneumothorax PERCUSSION NOTE • • • • DULL: Consolidation Collapse Pleural effusion (stony dull) • • • • IMPAIRED: Fibrosis Cavitation Bronchopneumonia • • • HYPER-RESONANT (presence of air): Pneumothorax emphysema VOCAL RESONANCE The prolongation and intensification of sound produced by transmission of its vibrations to a cavity • Increased: Air present in the alveoli/ consolidation/ fibrosis in the lung parenchyma e.g, Pneumonia, bronhiectasis • Decreased: Fluid or air present in pleural space e.g, pleural effusion, pneumothorax BREATH SOUNDS Increased: • Consolidation • Interstitial lung disease (prolonged expiration) Decreased: • Collapse • Local fibrosis • Pleural effusion or empyema Vesicular (prolonged expiration): • Bronchitis • Asthma • Pneumonia • emphysema WHEEZING • Wheezing is a high-pitched whistling sound during breathing. • It occurs when air flows through narrowed breathing tubes Inspiratory wheeze: • Bronchitis • Pneumonia Expiratory wheeze: • Asthma • Emphysema CREPITATIONS A noise produced by pressure upon tissues containing abnormal amounts of air, the rubbing of fractured ends of bones, and by cracking joints Causes: • Consolidation • Localized fibrosis • Cavitation • Pneumothorax • Pneumonia REFERENCES • Davidson’s Principles and Practice of Medicine • Hutchison’s Clinical Methods • Medlineplus.com • Britannica online dictionary • Merriam-Webster dictionary