CLINICAL PRIORITY ACCESS CRITERIA
advertisement
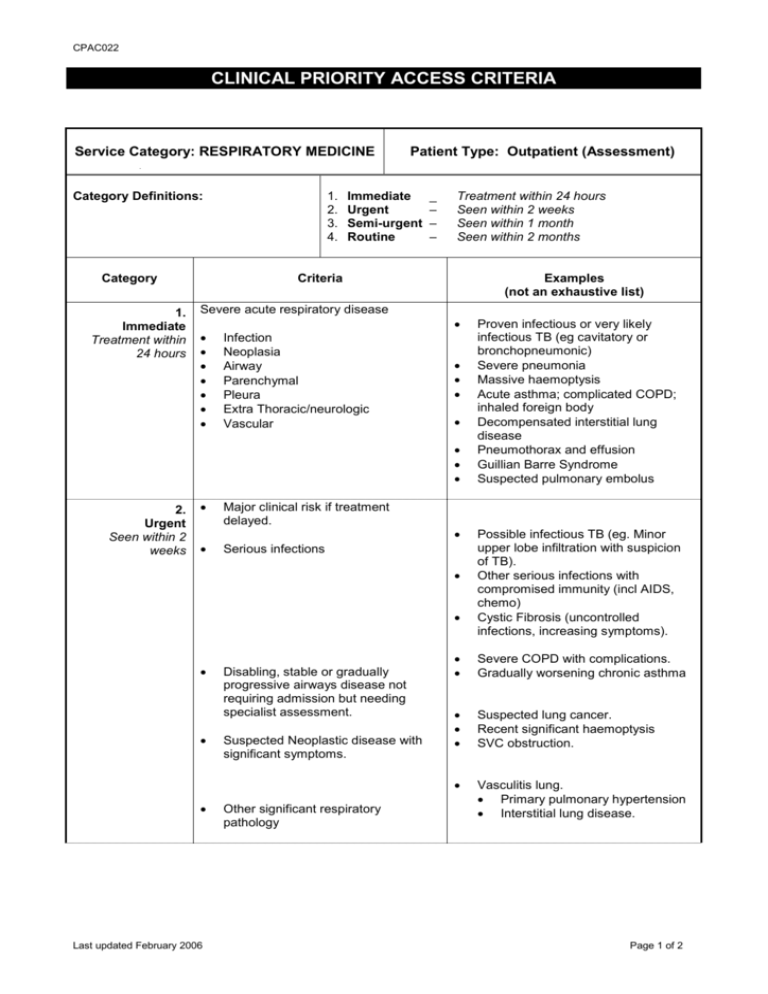
CPAC022 CLINICAL PRIORITY ACCESS CRITERIA Service Category: RESPIRATORY MEDICINE Category Definitions: Category 1. Immediate Treatment within 24 hours 1. 2. 3. 4. Patient Type: Outpatient (Assessment) Immediate Urgent Semi-urgent Routine _ – – – Treatment within 24 hours Seen within 2 weeks Seen within 1 month Seen within 2 months Criteria Examples (not an exhaustive list) Severe acute respiratory disease Infection Neoplasia Airway Parenchymal Pleura Extra Thoracic/neurologic Vascular 2. Urgent Seen within 2 weeks Major clinical risk if treatment delayed. Serious infections Last updated February 2006 Disabling, stable or gradually progressive airways disease not requiring admission but needing specialist assessment. Suspected Neoplastic disease with significant symptoms. Other significant respiratory pathology Proven infectious or very likely infectious TB (eg cavitatory or bronchopneumonic) Severe pneumonia Massive haemoptysis Acute asthma; complicated COPD; inhaled foreign body Decompensated interstitial lung disease Pneumothorax and effusion Guillian Barre Syndrome Suspected pulmonary embolus Possible infectious TB (eg. Minor upper lobe infiltration with suspicion of TB). Other serious infections with compromised immunity (incl AIDS, chemo) Cystic Fibrosis (uncontrolled infections, increasing symptoms). Severe COPD with complications. Gradually worsening chronic asthma Suspected lung cancer. Recent significant haemoptysis SVC obstruction. Vasculitis lung. Primary pulmonary hypertension Interstitial lung disease. Page 1 of 2 CPAC022 3. Semi-Urgent Seen within 1 month Major/moderate function impairment with moderate clinical risk requiring assessment and review. Less severe variants of Cat. 1 Major GP diagnostic respiratory dilemmas Disorders of excessive sleepiness. Extra-pulmonary thoracic disorders. Other categories of TB i.e. extrapulmonary, smear –ve, +ve urine culture, +ve histology Assessment for domicilliary oxygen Dyspnoea of uncertain cause Respiratory disease associated with complicating extra pulmonary disease Severe OSA Respiratory muscle impairment Major chest wall deformity Extensive pleural disease 4. Routine Seen within 2 months Paediatric – adult transfer Past history suggests moderate functional impairment where clinical assessment and review may be beneficial. TB contacts Last updated February 2006 Cystic Fibrosis Moderate Obstructive Sleep Apnoea Moderate COPD Pleural Plaques “Stable” radiologic abnormalities Chronic Cough Asymptomatic parenchymal disease Mantoux +ve healthcare workers, other TB contacts, Refugees (This is currently a Public Health responsibility – Perth Chest Clinic, Ph 9325 3922) Page 2 of 2











