Whooping Cough (Pertussis) for patients
advertisement

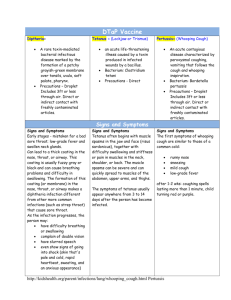
Whooping Cough (Pertussis) Information Leaflet for Patients What is whooping Cough? Whooping cough (sometimes called Pertussis) is s severe respiratory infection caused by bacteria. It is most common in children under the age of 1 year but can occur at any age. What are the symptoms of Whooping Cough? Whooping cough starts like cold with blocked nose, sneezing, mild fever and occasional cough that later develops into repeated severe coughing attacks. Cough can be followed by vomiting, incontinence and/or “whooping” sound at the end of each attack. The cough can be worse at night and can last for many weeks to months. Some newborns don’t cough at all but may stop breathing and turn blue, have feeding difficulties or they can choke and gag. Treatment Early diagnosis and antibiotic treatment of infection is important. Antibiotic treatment is necessary to prevent spread to others. Antibiotic treatment early during this infection may prevent severe illness. Prevention Whooping Cough is most contagious 2 to 4 days before the cough starts so the most effective prevention is through immunization. Vaccine is given to babies at 2, 4, 6 months of age and later at 45 year preschool children. A booster dose is recommended at 11-14 years. Doctor may prescribe antibiotics and/or vaccine to those who are in close contact with an infectious person. Whooping Cough is spread by direct close contact with an infected person therefore people diagnosed with whooping cough should stay at home until no longer infectious (3 weeks after symptoms develop or when antibiotic course completed). If you are concerned about your health or your babies health please contact your GP or hospital infection control team. Infection Control, Sep. 2012