Recombinant HSV vectors
advertisement

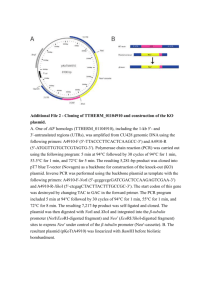
SPPLEMENTAL METHODS Recombinant HSV vectors. In order to obtain the gC promoter, genomic DNA from HSV-1 strain 17 was digested with two restriction enzymes, PstI and BamHI. Plasmid pSKgC(17) was generated by inserting the 2.46-kb PstI-BamHI fragment that contains UL44 (glycoprotein C, gC) into pBluescript II SK(-) plasmid (Stratagene, La Jolla, CA). The promoter region of UL44 (gC), including the initiation element (Inr), the TATA box and DAS binding factor sites, is described in (http://darwin.bio.uci.edu/~faculty/wagner). E.K. Wagner’s homepage The gC promoter was amplified from pSKgC(17) with the following pair of primers: forward primer (T7 primer: 5’GTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGC-3’) and reverse primer (5’- GTCGACGCGTGCCCGACGCCTCCCCCTCGC-3’), which contains SalI and MluI sites at the 5’ end. The amplified gC promoter fragment (0.5 kb) was electrophoresed and extracted from the gel by using QIAquick gel extraction kit (QIAGEN, Valencia, CA). The IE4/5 promoter was obtained from the pHGCX HSV amplicon vector plasmid.1 Firefly luciferase (Fluc) and Renilla luciferase (Rluc) cDNAs were obtained from pGL3-Basic Vector and phRluc/SV40 Vector (Promega, Madison, WI), respectively. Each luciferase gene was combined with either IE4/5 promoter or gC promoter, generating four shuttle plasmids, pT-gC-Fluc, pT-gC-Rluc, pT-IE4/5-Fluc, and pT-IE4/5Rluc. The methods for engineering recombinant HSV (HSVQuik system) have been previously described.2,3 Briefly, each shuttle plasmid and FLP-expressing helper plasmid (pFTP-T) were electroporated into bacteria containing the HSV-BAC construct (fHsvQuik-1). The resulting co-integrates of fHsvQuik-1 and the shuttle plasmids were then co-transfected into Vero cells with the CRE-expressing plasmid (pc-nCre). This generated the four recombinant viruses: rQ1-γ2-Fluc, rQ1-γ2-Rluc, rQ1-α-Fluc and rQ1α-Rluc. The green fluorescent protein (GFP) cDNA was inserted in-frame with the remaining 5’-coding sequence of the deleted UL39 (ICP6) sequence, thus generating recombinants that express GFP as a marker of infection. Viruses were propagated and titered in Vero cells as previously described.2 REFERENCES 1 2 3 Saeki Y, Breakefield XO, Chiocca EA. Improved HSV-1 amplicon packaging system using ICP27-deleted, oversized HSV-1 BAC DNA. Methods Mol Med 2003; 76: 51-60. Kambara H, Okano H, Chiocca EA, Saeki Y. An oncolytic HSV-1 mutant expressing ICP34.5 under control of a nestin promoter increases survival of animals even when symptomatic from a brain tumor. Cancer Res 2005; 65: 28322839. Terada K, Wakimoto H, Tyminski E, Chiocca EA, Saeki Y. Development of a rapid method to generate multiple oncolytic HSV vectors and their in vivo evaluation using syngeneic mouse tumor models. Gene Ther 2006.