Course Description - Department of LD
advertisement

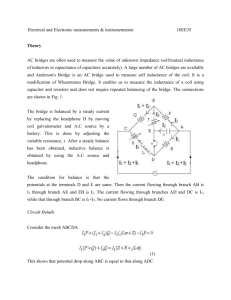
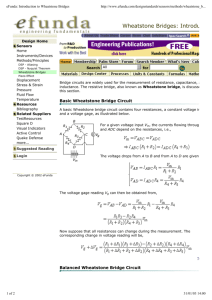
COVENANT UNIVERSITY, CANAAN LAND, OTA. EEE520 COURSE COMPACT College: College of Science and Technology School: School of Engineering and Technology Department: Electrical and information Engineering Programme: Electrical and Electronics Engineering Course Code: EEE520 Course Title: Advanced Instrumentation Units: 2 Course Lecturer: Engr. Ademola Abdulkareem. Semester: Omega Session: 2014/2015 Time: 2hrs/week Location: EIE Large Classroom Course Description: Revision of basics of measurement and instrumentation, Error in measurements, DC and AC bridges and their applications, Instrument transformers and applications in power systems, energy meters and metering, Electronic Instrumentations:: digital techniques, Analog/digital signal processing (ADC/DAC), sample and hold circuits, electronic counters and their applications, Application of microcontrollers in digital instrumentation. Course Objectives/Goals: At the end of the course students are expected to be able to: Have a thorough knowledge of electrical instrumentation measurement so as to adopt a practical approach to his measurement problems. Describe the types of instrument and know the importance of measurements in Electrical and information Engineering. Successfully measure electrical quantities and other line parameters (ie resistance, capacitance and inductance) in terms of fundamental units. Analyze instrument error and determine the limit of uncertainty in physical measurement. Identify, analyse and describe the dc potentiometer and dc Wheatstone bridge instruments to determine the value of unknown quantity in measurement. Understand the principle and application of dc Wheatstone bridge to locate cable fault in a cable manufacturing sector. Explain the limitation of Wheatstone bridge in the measurement of resistance. Analyse the Wheatstone bridge in unbalanced mode. Understand the operation principle of strain gauge and transducer application in unbalanced bridge. Identify and understand the general principle to obtain a balance in some classic inductance and capacitance ac Wheatstone bridges. State the advantages and uses of instrument transformer. Describe with illustrations, the principle of operation of current and voltage transformer. Explain why the secondary winding of a current transformer should not be open circuited while the primary is carrying current. Determine the ratio and phase angle errors of a relay current transformer. 1 Describe the induction-type energy meter. Describe with illustration, the principle of operation of dynamometer wattmeter for measurement of power. Understand and explain the measurement of power in a single-phase circuit and the use of three-phase wattmeter to measure three-phase circuit. Understand and explain the measurement of power in a three-phase circuit using Onewattmeter Method, Two-wattmeter method and Three-wattmeter method. State the advantages of electronic instruments in measuring technology Explain the elements of a digital acquisition system in the process of converting analog signal to digital signal. Understand the application of digital systems and microcontroller used for measurement systems and control. Methods of Lecture Delivery: Lectures will be delivered with the aid of multimedia power point presentation. A combination of lectures, tutorials and static presentation: use of white board and markers. Course Outlines: Modules 1.0 BASIC CONCEPTS 1.1 Revision of basics of measurement and instrumentation 1.1.1 Error in measurement 2.0 MEASUREMENT OF LINE PARAMETERS 2.1 Measurement of resistance 2.2 Measurement of low resistance. 2.2.1 Ammeter/Voltmeter method. 2.2.2 Potentiometer method 2.2.3 Kelvin Double Bridge 2.3 Measurement of medium resistance 2.3.1 Ammeter/Voltmeter method 2.3.2 Wheatstone bridge. 2.3.2.1 Errors in bridge arms. 2.4 Measurement in high resistance 2.4.1 Modified Wheatstone bridge 2.4.2 Loss of charge method 2.4.3 The megger tester 2.4.3.1 Megger tester for cable insulation resistance measurement. 2.5 Application of Wheatstone bridge-test to locate cable fault 2.5.1 Murray loop test 2.5.2 Varley loop test 2.5.3 Fall of potential test 2.6 Unbalanced bridge 2.6.1 Sensitivity of galvanometer 2.7 AC Bridges 2.7.1 Maxwell bridge. 2.7.2 Desualty bridge (measuring capacitance) 2.7.3 Wien bridge 2.7.4 Schering bridge 2.7.5 Owen bridge 2.7.6 Heaviside bridge 2 Week 1 Week 2-4 Week 5 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.2.1 3.3 3.4 3.4.1 3.4.2 3.5 3.5.1 3.5.2 .3.5.3 3.5.4 INSTRUMENT TRANSFORMER AND APPLICATION IN POWER SYSTEMS. Week 6&7 Voltage or Potential transformer (VT or PT). Current transformer. Precaution to be taken while using CT. Error in current or potential transformer. Energy meter and metering. Week 8&9 The Dynamometer wattmeter. The Induction-Type energy meter. Energy Meter - Measurement of power in single phase circuit. Measurement of power in three-phase circuit using one-wattmeter method. Measurement of power in three-phase circuit using two-wattmeter method Measurement of power in three-phase circuit using three-wattmeter method Measurement of power in three-phase circuit using three –phase wattmeter. 4.0 4.1 4.1.1 4.1.2 4.2 4.3 4.3.1 4.3.2 4.3.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 ELECTRONIC INSTRUMENTATION SYSTEM. Digital instruments Digital techniques measuring systems. Application of digital techniques to digital voltmeters (DVMs) Analogue techniques Analogue/digital (A/D) signal processing. Sampling process Analog-to-digital conversion (ADC) Resolution Sample-And-Hold Circuit (S/H) Electronic Counters and Their Application Application of Microcontroller in Digital instrumentation. Week 10-12 Tutorials: Tutorials class will be organized at the end of each course module and students are expected to make contribution in solving tutorial questions. Methods of grading: Continuous Assessments; Tests, Quiz and Assignments = 30% Examination = 70% Ground rules and Regulations: Attendance is compulsory; a minimum of 75% class attendance is required. Absolute concentration is required of all students during lectures. Topics for term papers / Assignments / Students activities: Assignment will be given when necessary and students are expected to make contribution during lecture hours. Alignment with Covenant University vision / Goals: The advanced instrumentation concern with the description of instruments and their attributes so that the magnitudes of and variation in, electrical, mechanical, and other quantities may be monitored in an optimized manner for any measurement situation. The knowledge and experiences acquired in this course is essential for the practicing engineer to have a thorough knowledge of electrical instrumentation and measurement systems. This is especially so since in addition to his own requirements, he may be called upon to advise others who have no electrical knowledge at all. Therefore the area of application of this course meet the practical everyday need and will be valuable to the new generation of Electrical Engineer to be raised. 3 Contemporary issues / Industry relevance: Advanced Instrumentation is primarily intended to assist the student following an electrical or electronic engineering degree course to adopt a practical approach to his measurement problems. It will also be of use to industrial engineer or technician, who finds himself involved with measurements in terms of volts, amperes, ohms, watts, etc, and faced with an ever increasing variety of instruments from a simple pointer instrument to a complex computer-controlled system. The course is aimed at practical conditions and situations rather than theoretical nicety hence help the engineer or instrument user, to select the right form of instrument for an application, and then analyze the performance of the competitive instruments from the various manufacturers in order to obtain the optimum instrument performance for each measurement situation. Recommended Textbooks: Sawhney, A.K., A Course in Electrical and Electronic Measurements and Instrumentation, Dhanpai Rai and Co, Naisarak, Delhi, 2008. Alan Symonds, Electrical Power Equipment and Measurements, MicGraw-Hill Companies (UK), latest edition Gupta, J.B., An Integrated course in Electrical Engineering, 4th edition, S.K. Kataria and Sons, New Delhi, 2010 Salawu, R.I., Principle of Electrical Engineering and Measurements, latest edition. . 4