Chapter 1
advertisement

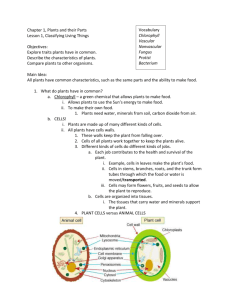
Chapter 1 Classifying Living Things Lesson 1 The Basic Unit of Life MAIN IDEA All living things are made of cells, the basic unit of life. Vocabulary 1. organism- Any living thing that is capable of life. 2. cell- The smallest unit of an organism. 3. chlorophyll- A green chemical in plants that allows the plant to use the Sun’s energy for making food. 4. tissue- A group of similar cells that work together at the same job. 5. organ- A group of tissues that work together to do a certain job. 6. organ system- A group of organs that work together to do a certain job. Other Important Information… What is the basic unit of life? o A cell The process of life must be carried out by the cells. Cells have structures that carry out different jobs (like; making food, releasing energy, and transport materials). Different organisms have different cells (like; plants and animals). *See Venn Diagram* What are living things made of? o Cells Some organisms have one cell, other organisms have many cells. Different kinds of cells do different jobs. Each cell helps out with the health and survival of the organism in a different way. Tissues-similar cells that have the same job Examples in Plants o strings that transport water and minerals from the roots to the leaves of the plant. o flesh of fruit protects the plant’s seeds. Examples in Animals o muscles that help you move o muscle, bone, skin, nerve and blood Organs- different kinds of tissues Examples in Plants o Stalks, fruits Examples in Animals o the heart, the lungs, and the brain. Organ system- group of organs that work together Examples in Plants o the roots of the plant are the main organ in the root system. o the stems and leaves are organs of the shoot system. Examples in Animals o a fox’s digestive system includes its mouth, stomach, and intestines. o organ systems work together to help the breathing process and digestion that keep you healthy and alive. What traits are used to classify organism? o patterns classification- the science of finding patterns among living things. o cells are used in classification. o cells from different organisms are different. o when you classify organisms the cells, tissues, organs and systems all have to be compared carefully. Lesson 2 The Kingdom of Life MAIN IDEA Living things are classified into kingdoms. Vocabulary 1. vascular- composed of or containing vessels. a. Vascular tissues- tubes that allow water from the plants roots to move up one set of tubes towards the leaves, flowers and other parts, while foods made in the leaves are moving down the other set of tubes to other plant parts. 2. nonvascular- plants that do not have vascular tissues. 3. vertebrates- animals that have backbones. 4. invertebrates- animals that do not have backbones. 5. fungus- member of a kingdom that have one celled and many celled living things that absorb food from their environment. 6. protist- member of a kingdom that contains one-celled and many-celled living things, some that make food and some that hunt for food. 7. bacteria- the tiniest living things. Other Important Information A kingdom is the largest subdivision of living things. Plants can be divided into two large groups; vascular and nonvascular. Each group is called a division. Vascular tissues- tubes that allow water from the plants roots to move up one set of tubes towards the leaves, flowers and other parts, while foods made in the leaves are moving down the other set of tubes to other plant parts. Example of vascular plants o trees and flowering plants Example of nonvascular plants o Mosses, Hornworts, Liverworts What makes animals different from plants? o animals cannot make their own food. o animals move from one place to another at some point. All animals are grouped into one kingdom. The animal kingdom. The animal kingdom is divided into two large groups. Vertebrates and invertebrates. What is a fungus? o one celled or many celled living thing that absorbs food from their environment. Fungi is the plural of fungus. Fungi is both useful and harmful for us. o Useful/good for: cooking, fighting diseases, help bread rise and breaks down decaying plants and animals in soil. o Harmful/bad- some poisonous, some spoil food, some smelly and some itchy like athletes foot. What is a Protist? o one-celled and many-celled living things, some that make food and some that hunt for food. Examples of Protist o Seaweed, algae, slime mold and diatoms. Protist provide food for many marine and freshwater animals. Others, like algae, contain chlorophyll and make their own food. All Protist have a nucleus- a dark, dense structure. Membrane- a thin envelope covering the nucleus. What are bacteria? o Tiniest living thing. Bacteria help animals and plants survive and also cause great trouble. Bacterium- a single cell without a nucleus.