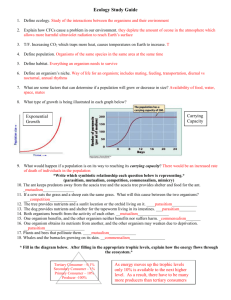
Diversity of Life Study Guide
advertisement

nucleus Control center of the cell. Contains DNA nuclearmembrane Surrounds and protects the nucleus. chromosomes Contains genetic information inside the nucleus in eukaryotic cells, throughout a prokaryotic cell. cellmembrane Surrounds the cell, lets some particles in and out. cellwall Provides structure and support in a plant cell. ribosomes Protein factories. endoplasmicreticulum Carries substances around the cell. chloroplasts Irregular shaped green organelle that allows for photosynthesis in plant cells. lysosomes Clean up the cell. vacuole Stores water and other substances for the cell. cytoplasm Jelly-like substance that organelles float in inside the cell. mitochondria The "powerhouse" of the cell - provide energy for the cell. living Something that is alive or was once alive - has the characteristics of life. nonliving Something that does not have the characteristics of life. organelle A part of a cell. paramecium A single celled organism that moves using cilia. euglena A single celled organism that moves using flagellum and is both heterotrophic and autotrophic amoeba A single celled organism that moves using pseudopod. elodea An aquatic plant that we looked at using microscopes. seedcoat The rigid outer covering of a seed. cotyledon Inside a seed, becomes the first leaf of a seedling embryo before a seedling germinates, it is known as an _____. vascular Tissue that transports fluids and nutrients in a plant. xylem Moves water and nutrients upward from the roots of the plant. phloem Moves sugars and other molecules downward from leaves of plants. germination When a plant grows from a seed. ovary Part of the pistil, the female reproductive organ of a flower. pistil Female reproductive part of a flower. stamen Pollen producing, male reproductive organ of a flower. petal Modified leaves, usually colorful, that surround the reproductive parts of a flower. monera Kingdom made up of prokaryotic, unicellular organisms, such as bacteria. Protist Kingdom made up of eukaryotic organisms, unicellular or living in colonies, such as algae and protozoan fungi Kingdom made up of spore producing eukaryotic organisms, such as mushrooms and mold. plant Kingdom made up of plants - both seeded and seedless. animal Kingdom made up of eukaryotic organisms that cannot make their own food, such as fish, birds, humans. adaptation The process in which an organism becomes better suited to its environment over many generations.