Perinatal Periods of Risk
advertisement

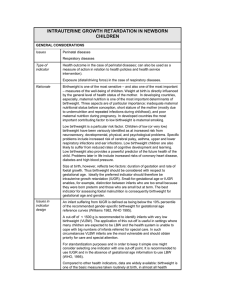
Perinatal Periods of Risk Practice Collaborative A CityMatCH, CDC, MCHB/HRSA & March of Dimes Initiative Methods, Definitions & Recommendations for PPOR Phase 1 Analysis 1. Study population: Live births and infant deaths (both 500 grams or larger birthweight) to resident mothers using the linked birth and infant death certificate file and fetal deaths (24 weeks or greater gestational age and 500 grams or larger birthweight) using the fetal death certificate file based on year of birth. Generally, place of residence at the time of birth defines inclusion in the study no matter where the place of residence at the time of death. Some communities limit place of residence at both birth and death. 2. Race/Ethnicity Groups: White non-Hispanic, Black non-Hispanic, Hispanic, American Indian, Hawaiian, Chinese, Japanese and other. If there is insufficient population size (less than 60 feto-infant deaths, or less than 10 deaths in any PPOR category) for a specific racial or ethnic group, the group should not be analyzed separately. Race and ethnicity are based on the race/ethnicity of the mother. 3. Maternal Age Groups: Less than 20 years, and 20 or more years. 4. Maternal Education Groups: 12 years or less, and more than 12 years. 5. Internal Reference Group: Generally, the reference group should be white non-Hispanic, 20 or more years of age with more than 12 years of education (if more than 60 feto-infant deaths occur among that population). In addition, a community may want to use some of other meaningful reference group from within the community or state or some national reference group. When the number of feto-infant deaths is less than 60, sometime an external reference group can be used instead. 6. Study Variables: Birthweight: If the birthweight is unknown, its value is imputed based on the gestational age by the following rule. For infant deaths, gestational ages < 31 weeks are treated as birthweight < 1,500 grams, and gestational ages < 22 weeks are treated as birthweight birthweight <500 grams. For fetal deaths, gestational ages < 32 weeks are treated as birthweight < 1,500 grams, and gestational ages < 24 weeks are treated as birthweight <500 grams. If both birthweight and gestational age are unknown, the death is excluded from study. Gestational age: Gestational age is defined by last menstratual period with unknowns replaced by clinical estimates. If the gestational age for a fetal death is unknown and the birthweight is known and 500 grams or more, its gestational age is assumed to be of 24 weeks or more gestation. 7. Data Quality: Places with greater than 10% missing of both birthweight and gestational age in fetal, infant or combined deaths, and places with greater than 10% imputed birthweight and/or gestational age have a major data quality issue. Caution is strongly recommended when using PPOR approach. Because the actual feto-infant mortality rates are underestimates. Places with greater than 10% unknown for some of maternal race/ethnicity, age and education variables, also have a major data quality issue. In order not to introduce bias, it is important to define the target/reference populations using other variables or use external reference groups. 8. Number of Events: Populations with fewer than 60 feto-infant deaths (or with less than 10 deaths in any of the four PPOR categories) experience substantial instability estimating their PPOR rates and it is difficult to accurately interpret the PPOR findings. The PPOR approach may not be the best approach for studying such populations. D:\401250585.doc