HIGH RISK NEWBORN: GOALS, CONCEPTS, PRINICPLES

NURSING MANAGEMENT
OF PRE-TERM AND
SMALL FOR DATES…..
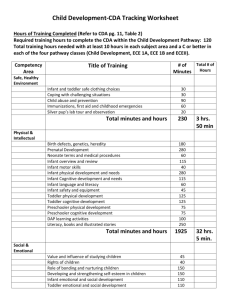
Classification of high risk infants
1. Classification according to size.
2. Classification according to gestational age.
3. Classification according to mortality.
New born assessment
Transitional assessment first period of reactivity second period of reactivity
Behavioral assessment
Physical assessment
Reflexes
Classification according to size
1. Low birth weight infant.
2. Very low birth weight infant.
3. Extremely low birth weight infant.
4. Appropriate for gestational age.
5. Small for date (SFD) infant or
6. Small for gestational age (SGA) infant.
7. Intra uterine growth restriction.
8. Large for gestational age infant.
Classification according to GA
1. Premature infant (preterm).
2. Full term infant.
3. Post mature infant (postterm).
Classification according to mortality
1. Live birth
2. Fetal death
3. Neonatal death
4. Perinatal mortality
5. Post natal death.
Pre-Term Definition.
A baby born before 37 completed weeks of gestation calculating from the first day of last menstrual period is arbitrarily defined as pre0term baby.
ETIOLOGY FACTORS
SMOKING
Cervical incompetence
Fetal Stress
Face & Head
Skin & Subcutaneous
Genitals
Central nervous system
Respiratory System
Cardio vascular system
Gastro intestinal system
Initial assessment
APGAR Score
Clinical assessment
Intra uterine growth chart.
Immediate care clear the airway
PRE TERM CARE
Positioning of the baby.
Thermal comfort
Oxygen supply
Phototherapy
Polythene cover
Infection: closed port
Tactile stimulation
Nutrition : TPN Therapy
Nutritional line
Weight record
Kangaroo care
Umbilical cord care
Eye care
Diaper care
Hypoglycemic management
Mother’s Role…….
Partner’s support
Difference’s
Take home message
There is no evidence in human biology which tells us so much about the past events and the future trajectory of life, as the weight and time of the infant at the time of birth.
By: V.Ramalingaswami.