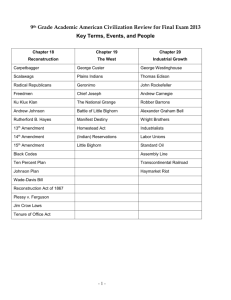
1920`s Quiz - TeacherWeb
advertisement

Great Depression Quiz 1) Which situation was a basic cause of the Great Depression? (1) continued increases in wages for workers (2) excessive profits for farmers (3) overregulation of the stock market (4) overproduction of consumer goods 2) In the 1930's, one factor that accounted for the westward migration of farmers from the Great Plains was (1) high farm prices (3) the Dust Bowl (2) new technologies (4) the baby boom 3) An important factor contributing to the start of the Great Depression in the United States was the (1) increase in military spending (2) failure to maintain the gold standard (3) reduction of tariff rates (4) uneven distribution of wealth 4) Which conditions are most characteristic of an economic depression? (1) high unemployment and overproduction (2) large business investments and low taxes (3) too much money in circulation and high stock prices (4) high employment and increased real estate investments 5) After the election of 1932, a friend told President Franklin D. Roosevelt that if he succeeded he would go down in history as the greatest American President. Roosevelt replied, "Yet if I fail, I may be the last one." This response reflected President Roosevelt's belief that the 1) Constitution limited him to two terms in the Presidency 2) military was seriously considering a takeover of the government 3) Great Depression threatened the people's faith in democracy 4) American people were opposed to major changes in the role of government 6) The New Deal tried to solve many problems of the Great Depression by (1) providing federal aid to many sectors of the economy (2) reducing taxes on big business to stimulate job creation (3) lowering federal spending to maintain a balanced budget (4) decreasing foreign competition by raising tariffs 7) During the Great Depression, expressions such as Hoovervilles and Hoover blankets showed that President Hoover (1) was seen as a role model (2) used the military to aid the unemployed (3) was blamed for the suffering of the poor (4) supported relief and public housing for the needy 8) The National Labor Relations Act (Wagner Act) of 1935 strengthened labor unions because it legalized (1) collective bargaining (3) the open shop (2) blacklisting (4) the sit-down strike 9) The strongest opposition to President Franklin D. Roosevelt’s New Deal programs came from (1) western farmers (3) factory workers (2) business leaders (4) recent immigrants Base your answer to question 10 on the cartoon below and on your knowledge of social studies. 10) This cartoon illustrates that President Franklin D. Roosevelt caused a controversy based on (1) increased military spending in the early 1930s (2) a plan to assume some of the powers reserved to the states (3) efforts to counter the Dust Bowl with federal conservation measures (4) proposals that violated the principle of separation of powers 11) Which economic trend of the 1920s helped cause the Great Depression? (1) rising cost of mass-produced goods (2) increasing income tax rates (3) falling tariff rates (4) widening income gap between the rich and the poor 12) The Supreme Court declared some New Deal laws unconstitutional because these laws (1) overextended the power of the federal government (2) forced the federal government into heavy debt (3) ignored the rights of minority groups and women (4) failed to solve the problems for which they were intended 13) One difference between the administrations of President Franklin D. Roosevelt and President Herbert Hoover is that Roosevelt was (1) unwilling to allow government agencies to establish jobs programs (2) unable to win congressional support for his economic program (3) able to ignore economic issues for most of his first term in office (4) more willing to use government intervention to solve economic problems 14) The National Labor Relations Act (Wagner Act) of 1935 gave labor unions the right to (1) represent workers in collective bargaining (2) insist on an open shop in the workplace (3) establish quotas on immigration (4) use blacklists and yellow dog contracts 15) President Franklin D. Roosevelt’s response to Supreme Court decisions that declared several New Deal laws unconstitutional was to (1) ask Congress to limit the Court’s jurisdiction (2) propose legislation to increase the size of the the court (3) demand the resignation of several justices (4) ignore the Court’s rulings 16) One similarity between President Franklin D. Roosevelt and President Lyndon B. Johnson is that both 1. believed strongly in States rights 2. expanded the power of the Presidency 3. supported a strict construction of the Constitution 4. opposed most civil rights legislation 17) In the 1930s, President Franklin D. Roosevelt changed the federal government’s role in the economy by (1) reducing programs to help the unemployed (2) ending efforts at trust busting (3) raising tariffs to protect domestic industries (4) using deficit spending to stimulate economic growth 18) President Lyndon B. Johnson’s Great Society is similar to President Franklin D. Roosevelt’s New Deal in that both programs (1) sought ratification of the Equal Rights Amendment to guarantee equality for women (2) advocated passage of civil rights laws to help African Americans (3) supported federal funding of programs for the poor (4) approved efforts by states to reduce taxes for the middle class Base your answers to questions 19 and 20 on the cartoon below and on your knowledge of social studies. 19) To try to correct the problem shown in the cartoon, President Franklin D. Roosevelt proposed (1) increasing the number of justices on the Supreme Court (2) raising the salaries of federal judges (3) reducing the Supreme Court’s use of judicial review (4) exercising his veto power over Supreme Court decisions 20) President Roosevelt’s attempt to correct the problem shown in the cartoon resulted in (1) the quick end of New Deal reforms (2) resignations of several federal judges (3) congressional rejection of the president’s proposal (4) a decrease in the authority of the Supreme court