Kingdoms
advertisement

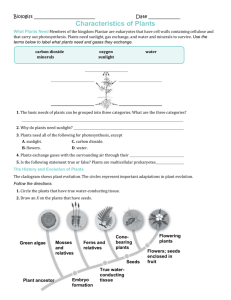
NAME:_________________________________PERIOD:_______DATE:_______________ Classification / Taxonomy / Systematics Review DOMAINS 1. Draw a phylogenetic tree (an evolutionary tree diagram) illustrating the relationship between the three domains. 2. In the table below outline the key characteristics that distinguish the three domains. Include examples of organisms in each domain. Domain Bacteria (Eubacteria) Archaebacteria Eukarya Characteristics Example Eukaryotic Kingdoms In the table below outline the key characteristics that distinguish the four kingdoms of the Domain Eukarya by making notes on the following: (1) mode of nutrition, (2) presence or absence of cell wall, (3) method(s) of reproduction, and 94) any other notable characteristic. Kingdom Mode of Nutrition Cell Wall Protista cell wall (cellulose) Plantae heterotrophs Other some have cell wall some have only cell membrane diatoms & forams have silica (glass) cell walls Fungi Animalia Reproduction mostly sexual + and - strains asexual for unicellular yeast photoplankton & zooplankton locomotion via flagella, cilia, pseudopods mostly unicellular & some multicellular Ex: euglena, amoeba, paramecium, kelp Eukaryotes: Plants In the table below outline the key characteristics that distinguish the four groups of land plants by making notes on the following: (1) presence or absence of vascular system, (2) dominance of gametophyte vs. sporophyte, (3) mode of reproduction, and (4) any other notable characteristics. Plant Group Vascular System Gametophyte & Sporophyte Reproduction Other flowers animal pollinators double fertilization seeds in fruit monocots dicots (eudicots) dominant gametophyte dependent sporophyte Bryophytes (mosses) Pteridophytes (ferns) Gymnosperms (conifers) Angiosperm (flowering) Yes tracheophytes dominant sporophyte highly reduced gametophyte male gametophyte in pollen female gametophyte in ovule In the table below outline the key characteristics that distinguish the groups of the Kingdom Animalia by making notes on the following: (1) common name & examples, (2) type of symmetry, (3) no coelom, pseudocoelom, or coelom, (4) saclike or tublike gut, (5) soft body, exoskeleton, or endoskeleton, and (6) any other notable characteristic (e.g. proto- vs deutersotome, etc). Phylum Porifera Common Name & Examples Symmetry Coelom Body Plan (Gut Type) none soft body Platyhelminthes pseudocoelom Nematoda bilateral segmented protostome Annelida tubelike Arthropoda Echinodermata Chordata Phylum Characteristic none Cnidaria Mollusca Body Type radial endoskeleton (calcium plates) Eukaryotes: Animals: Vertebrates (Chordates) In the table below outline the key characteristics that distinguish the five subgroups of the Vertebrates by making notes on the following: (1) common name and examples, (2) body structure & type of body covering, (3) structure used for gas exchange, (4) structure of heart, (5) ectotherm vs. endotherm, (6) mode of fertilization, (7) mode of development, (8) any other notable characteristic. Subgroups Common Name & Examples Body Gas Exchange Ecto- VS. Endotherm Fertilization Development Characteristic ectotherm external external aquatic egg metamorphosis First land animal First tetrapods 2 chambers Fish Amphibian Heart frogs salamander wet skin lungs & skin 3 chambers external amniotic egg Reptilia internal Aves hair Mammalia Eukaryotes: Animals: Vertebrates: Mammals In the table below outline the key characteristics that distinguish the 3 subgroups of the Mammals by making notes on the following: (1) mode of development, (2) care of the young, (3) any other notable characteristic. Also include examples of organisms in each subgroup. Mammal Subgroup Montremes Marsupials Placentals Characteristics Example