LIFE CYCLES OF PLANTS - Teaching Biology Project

ALTERNATION OF
GENERATIONS
1.
Alternation of generations : haploid (n) stage that produces gametes followed by diploid
(2n) stage producing spores.
2.
Haploid : gametes; half the number of chromosomes in somatic cell, indicated by n, result of meiosis.
3.
Diploid : somatic cells; double number of chromosomes in gametes, indicated by 2n; result of fertilisation.
1.
Gametophyte : generation producing gametes in gametangium/ gametangia sexual stage.
2.
Sporophyte : generation producing spores in sporangium/ sporangia – asexual stage.
NB: In higher plants the generations alternate in the life cycle of a plant; in lower plants reproduction is either through gametes
(sexual) or spores etc. (asexual).
1.
A haploid gametophyte generation that produces gametes (n) by mitosis ...
the gametes (n) fuse to form zygote (2n), the start of ...
2.
A diploid sporophyte generation that produces spores (n) by meiosis.
1.
2.
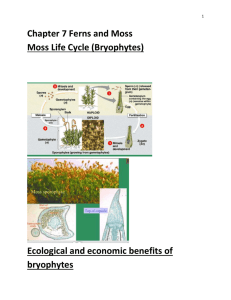
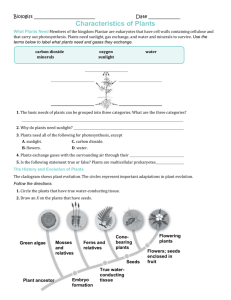
Mosses (Bryophyta)
Ferns (Pterophyta/ Pteridophyta)
Seed plants (Spermatophyta)
Gymnospermae (cone-bearing plants producing seeds)
Angiospermae (flowering plants producing seeds)
Exam guidelines require study of mosses and flowering plants to highlight alternation of generations.
Leaf-like structures of moss gametophyte
Sporangium of moss sporophyte
Fern leaf (sporophyte) with sori (groups of sporangia
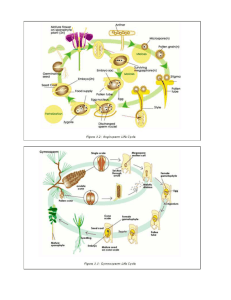
GYMNOSPERMS
ANGIOSPERMS
Gymnosperms have two types of sporangia – female and male
Female cones at different ages Male cones
Mosses Ferns, gymnosperms and flowering plants
Gametophyte dominant
Sporophyte dominant