3rd Grade Earth Movements
advertisement

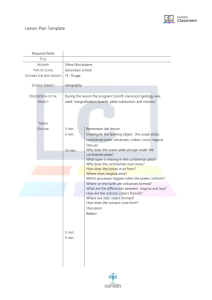
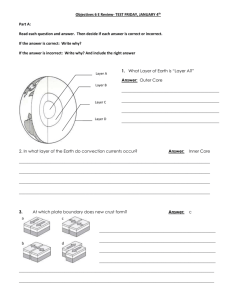
3rd Grade Earth Movements Content Standard IV: Earth Essential Learnings: What do students need to know and be able to do? Big Ideas: 1. Experimental Design (observations, question, hypothesis and design) Students will….. 2. Scientific testing (conduct investigations, collect and organize data) Explore the Massive movements that are constantly shaping the Earth. Learn how fossils/rocks provide evidence about the plants and animals and clues to Earth’s history, structure, environment and geological activity. 3. Analysis and Conclusions (analysis trends, and conclusions) 4. Composition and structure of Earth Construct Earth cross-sections to compare ocean and continental crusts. Investigate Earth processes that lend support to the theories of continental drift and plate tectonics. Model ocean-floor spreading, plate subduction, magma convection currents, volcanism, and earthquakes at plate boundaries. Essential Vocabulary: Continent Mantle Plate Core Mid Ocean Ridge Ocean Floor Spreading Trench Subduction Continental Crust Plate Boundary Fossil Volcano Convection Continental Drift Earthquake How will we effectively teach to ensure students learn? Inquiry High Yielding Instructional Strategies embedded in each investigation below Page 1 of 3 Earth Movements Activity 1: Our Earth Essential Question: What are the properties of each layer of the Earth? Activity 2: The Earth’s Crust Activity 4: Convection Currents Activity 3: Rock: Clues to the Past Activity 5: Continents Adrift Essential Questions: Activity 6: Plates in Motion What are the geographic features found in oceanic and continental crust? Essential Questions: How do rocks provide scientists with clues about the history and structure of the Earth? Activity 7: OceanFloor Spreading Activity 8: Subduction What causes convection currents? What causes continents to move? Activity 9: Building Mountains Activity 10: A Model Volcano Essential Question: Activity 11: The Vibrating Earth How do mountains form? Activity 12: The Ring of Fire Essential Questions: How do mid-ocean ridges form? How do ocean trenches form? How do we know if students are learning? Assessment: Use Copy Masters section in the Delta Teacher’s manual Page 2 of 3 Earth Movements Essential Questions: How does temperature affect a gas under pressure? What causes volcanic eruptions? What causes earthquakes? Why do volcanoes and earthquakes occur at plate boundaries? What will we do if students don’t learn or if they are already performing at or above grade level? Science Extension opportunities provided in teachers manual Reteaching Strategies Suggested Time Frame: 19 sessions 45 minutes each Scope and Sequence: Students will only have personal experiences with earth movements and composition of the Earth. DRAFT 5/8/2009 Page 3 of 3 Earth Movements