Heat Sources
advertisement

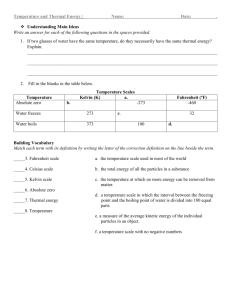
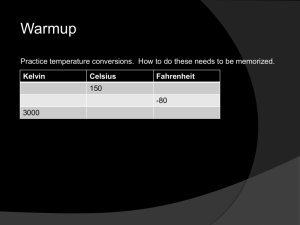
Thermal Energy Outline IN this chapter we will define and study thermal energy and how it is affected by the behavior of atoms. We will examine the basic concepts of observing, measuring, conserving, and using thermal energy in your everyday life. Let’s begin by reviewing some concepts that we already know. A. Mass is the amount of _________________ that makes up an object B. All matter is made of _______________________. a. These are the basic building blocks that make everything including _________________, __________________, and _____________________. b. Even powerful __________________________ are not strong enough to view any single atom because of their size. Understanding Thermal Energy begins with an understanding of the Kinetic Theory of Matter. ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ From this law we need to understand that: 1. Kinetic means _______________. 2. Atoms make up 3 states of matter. a. ______________ b. ______________ c. ______________ 3. Friction produces ______________. 4. The _______________ of atoms can be measured. 5. All heat that we feel is produced by the __________________ from atoms. a. Examples. i. _______________ ii. _______________ iii. _______________ iv. _______________ v. _______________ Temperature _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________ The unit for measuring temperature is the ____________________. Instrument for measuring temperature is the _________________________. Relies on expansion and contraction of liquids. 1. ______________________ (very dangerous) 2. ______________________ (preferred) Temperature can be measured using three different scales 1. _____________________ scale ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ 2. _____________________ scale ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ 3. _____________________ scale ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ The ____________________ scale was designed for __________________________ zero. It designates zero as the coldest possible temperature Absolute zero means _________________________ _______________________________________________________ Temperature Chart Celsius Fahrenheit Kelvin Freezing point H20 Boiling point H20 Body Temp. Room Temp. Absolute Zero Conversion formulas: Thermal Energy ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ Kinetic Energy - ______________________________ Potential Energy - _____________________________ Expansion and Contraction Materials will _____________________ when they are heated and _____________________ when cooled. ____________________- an increase in size ____________________- a decrease in size When a material is heated its particles _______________ into each other creating more space . This is expansion. When cooling, the particles move closer together causing _________________________. One exception to the rule_________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ ______________________________ can be installed to absorb expansion so damage can be prevented. ______________________ are used in : 1. __________________________________ 2. __________________________________ 3. __________________________________ Thermostat- _______________________________________________ Thermostats use a strip of metal called a_____________________, which allows appliances to be activated automatically. Examples: 1. ___________________________ 2. ___________________________ 3. ___________________________ Energy Transfer Heat _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ The _______________ is the unit for measuring heat. These are the same calories that you associate with food. Burning calories is the releasing of _______ _____________. There are 3 ways that heat energy can be transferred to objects. 1. _______________ 2. _______________ 3. _______________ Conduction - _______________________________________________ How does it happen? ____________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ Materials that are good ___________________of heat are: 1. _____________________ 2. _____________________ 3. _____________________ If the material is not a good conductor, it is called an _________________. Materials that are good insulators of heat are: 1. _____________________ 2. _____________________ 3. _____________________ Convection - ________________________________________________ When convection forms a continuous cycle, the moving air is called a ___________________________. Moving from hot to cool area Cooled air falls to ground Heat source Hot air is __________ dense than cold air, therefore it will always rise above it. Radiation or (Radiant energy)_____________________________________________________________ Examples of radiant energy are: 1. ________________________________ 2. ________________________________ 3. ________________________________ Amount of radiation that can be taken in by a material depends on the material’s ____________________. 1. Dark surfaces ____________________________________. 2. Light surfaces ____________________________________. 3. Transparent surfaces _______________________________ __________________________________________________. Temperature Scales 1. What is the freezing point of water in: O Fahrenheit O Celsius Kelvin 2. What is the boiling point of water in: O Fahrenheit O Celsius Kelvin 3. Room temperature is approximately 70OF. Calculate room temperature in: O Celsius Kelvin 4. Your body temperature is 98.6OF. Calculate body temperature in: O Celsius Kelvin 5. What is absolute zero and what temperature is it in: O Fahrenheit O Celsius Kelvin 6. What is the definition of temperature?
![Temperature Notes [9/22/2015]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006907012_1-3fc2d93efdacd086a05519765259a482-300x300.png)