Standardized Units: Problem Solving Assignment
advertisement

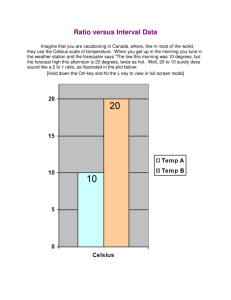
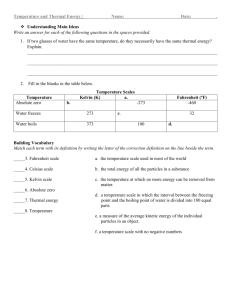
Chapter 2: Approaches to Problem Solving Assignment #2 – Unit 2B Standardized Units: More Problem-Solving Power Pgs. 101 – 112 1. Briefly describe the origin and use of common units in the U.S. Customary system. The roots of US Customary units reach back to ancient Middle Eastern civilizations. Foot was once the length of the foot of whoever was measuring; Inch comes from Latin “uncia” meaning “thumb-width”. Mile comes from Latin “milia passum” meaning “one thousand paces”. Yard – measurement from tip of nose to tip of thumb. Grain – based on the weight of a typical grain of wheat. 2. Briefly describe the origin and use of metric units. Invented in France late in the 18th century and now used throughout the world. Designed for 2 primary reasons (1) to replace many customary units with just a few basic units (2) to simplify conversions through use of a decimal system. *Powers of 10* 3. What are the basic metric units of length, mass, time, and volume? How are the metric prefixes used? length – meter *prefixes indicates multiplying by a power of 10 mass - kilogram time – second volume - liter 4. Using examples, show how to convert among the Fahrenheit, Celsius, and Kelvin temperature scales. Celsius to Fahrenheit: Multiply by 1.8. Then add 32. Fahrenheit to Celsius: Subtract 32. Then divide by 1.8 Celsius to Kelvin: Add 273.15 Kelvin to Celsius: Subtract 273.15 5. What is energy? List at least three common units of energy. Under what circumstances do the different units tend to be used? Energy us what makes matter move or heat up. 3 common units of energy: Calorie (measures the energy our bodies can draw from food), joule, watt, kilowatt-hour 6. What is the difference between energy and power? What are the standardized units for power? Power is the rate at which energy is used, which means it has units of energy divided by time. The most common unit of power is the width, defined as 1 joule per second. 7. What do we mean by density? What do we mean by concentration? Describe common units of density and concentration, including blood alcohol content, with examples. Density describes compactness or crowding. - material density (g/cm3) - population density (people/mi2) - info density (MB/in2) Concentration describes the amount of one substance mixed with another. - concentration of an air pollutant (ppm) - Blood alcohol content (gms./mL) Exercises in your textbook: pgs. 114 – 116 #’s 18 – 28 ; 29 – 44 ; 45 – 52 ; 53 – 58 ; 59 – 68 ; 69 – 70 ; 71 – 72 ; 75 ; 76 ; 77 – 82 Additional examples: p. 115 83, 85, 93, 94
![Temperature Notes [9/22/2015]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006907012_1-3fc2d93efdacd086a05519765259a482-300x300.png)