Thermal Energy Notes: Temperature, Heat Capacity, Calculations

Chapter 3: Matter and Energy
Section 4: Thermal Energy - Notes
Date:____________
Objectives:
Convert between Fahrenheit, Celsius, and Kelvin temperature scales.
Relate energy, temperature change, and heat capacity.
Thermal Energy:
The atoms and molecules that compose matter are in constant ___________________________
___________________________ o they contain _______________________________________
The ____________________________ of a substance is a measure of its thermal energy. o The _________________ an object, the greater the random motion of the atoms and molecules that compose it, and the ____________________ its temperature.
______________, which has units of energy, is the transfer or exchange of _________________
____________________ caused by a temperature difference. o When a piece of cold ice is dropped into a cup of warm water, heat (thermal energy) is transferred from the water to the ice.
______________________________, by contrast, is a measure of the thermal energy of matter
(not the exchange of thermal energy). o Measures the _____________________________________ of the molecules of matter.
Both cups of water are at the same temperature… o Which has a higher average kinetic energy? o Which contains more thermal energy?
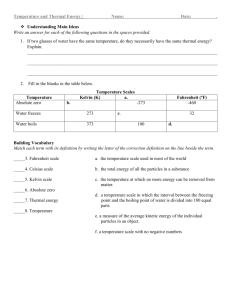
Temperature Scales:
The Fahrenheit scale was set according to the following standards o 0 °F to the freezing point of a concentrated ____________________________________ o 96 °F to _______________________________________________________.
On the Fahrenheit (°F) scale o water freezes at ___________ o water boils at ___________ o Room temperature is approximately ___________
On the Celsius (°C) scale: o water freezes at ___________ o water boils at ___________ o Room temperature is approximately ___________
The Kelvin (K) scale avoids _______________________ temperatures by assigning 0 K to the coldest temperature possible, _________________________. o Absolute zero is the temperature at which molecular motion _________________.
On the Kelvin (K) scale, o water freezes at ___________ o water boils at ___________ o Room temperature is approximately ___________
The Fahrenheit degree is ____________________ the size of a Celsius degree.
The Celsius degree and the Kelvin are the _________________________
We can convert between Fahrenheit, Celsius, and Kelvin temperature scales using the following formulas:
Practice: o Convert –25 °C to kelvin. o Convert 139 °C to Fahrenheit. o Convert 358 K to Celsius. o Convert 55 °F to Celsius. o o
Convert 310 K to Fahrenheit.
Convert –321 °F to kelvin.
Heat Capacity:
Heat capacity: The ________________________________ (usually in joules) required to change the temperature of a given amount of the substance by ___________
Specific heat capacity: the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of __________ of any substance by ___________ o Specific heat capacity has units of joules per gram per degree Celsius, ____________
Specific heat capacity is an _____________________________
Specific heat describes how well an object retains heat o A substance with a _______________________________ is quickly heated, but also quickly cools o A substance with a _______________________________ takes a long time to warm up, but will also retain that heat for a longer period
Styrofoam is a very poor conductor of heat; it is a good insulator. It has a
________________________________
Metals are good conductors of heat. They have
__________________________________
Heat Capacity Calculations:
q is ____________________________________________________
m is ___________________________________________________________________________
C is ___________________________________________________________________________
T is ___________________________________________________________________________ o The symbol Δ means the change in, so ΔT means the change in temperature.
Example: Gallium is a solid at 25.0°C and melts at 29.9°C. If you hold gallium in your hand, it can melt from your body heat. How much heat must 2.5 g of gallium absorb from your hand to raise its temperature from 25.0°C to 29.9°C? o The specific heat capacity of gallium is 0.372 J/g°C.
Practice: o The temperature of a lead fishing weight rises from 26°C to 38°C as it absorbs 11.3 J of heat. What is the mass of the fishing weight in grams? o A chemistry student finds a shiny rock that she suspects is gold. She determines that its mass is 14.3 g. She then finds that the temperature of the rock rises from 25°C to 52°C upon absorption of 174 J of heat. Find the heat capacity of the rock and determine whether the value is consistent with the heat capacity of gold (which is listed in Table
3.4). o A 328 g sample of water absorbs 5.78 × 10 3 J of heat. Calculate the change in temperature for the water. If the water is initially at 25.0°C, what is its final temperature?
The heat capacity of substance A is twice that of substance B. If samples of equal mass of the two substances absorb the same amount of heat, which substance undergoes the larger change in temperature?
![Temperature Notes [9/22/2015]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006907012_1-3fc2d93efdacd086a05519765259a482-300x300.png)