5 - Faculty of Information Technology Multimedia University
advertisement

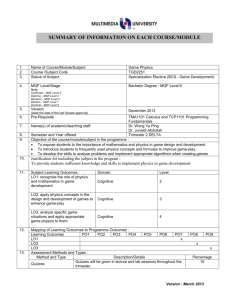
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Name of Course/Module Course Code Status of Subject MQF Level/Stage Note : Certificate – MQF Level 3 Diploma – MQF Level 4 Bachelor – MQF Level 6 Masters – MQF Level 7 Doctoral – MQF Level 8 Version (state the date of the last Senate approval) Pre-Requisite Name(s) of academic/teaching staff Artificial Intelligence TIC3151 Elective Bachelor Degree – MQF Level 6 Date of New Version : Year 2012 None Prof. Yashwant Prasad Singh Dr. Lee Chien Sing 8. 9. 10. 11. Semester and Year offered Trimester 1 (Beta Level) Objective of the course/module in the programme : The course aims to introduce the principles and methods in artificial intelligence as technical subject and its limitations, by working through numerous examples of how, when, and where to apply AI techniques. It also exposes the students to the search techniques, logic, knowledge representation techniques and alternate ways of representing knowledge and explore the consequences of the various representations in AI problem solving Subject Learning Outcomes : By the end of the subject, students should be able to Explain about intelligence, artificial intelligence and various AI-techniques Demonstrate a good understanding in agent technology, Ability to identify problems that can be expressed in terms of search problems or logic problems, and translate them into the appropriate form, and know how they could be addressed using an algorithmic approach. Ability to identify problems that can be expressed in terms of appropriate learning methodology for the problem area. Synopsis: To familiarize with several problem-solving techniques, mainly search and logic. Problem solving in artificial intelligence is done using LISP and logic programming. Memperkenalkan beberapa teknik penyelesaian masaalah, terutamanya, masalah gelintaran and logik. Penyelesaian masaalah dalam bidang kecerdasan buatan dilaksanakan dengan mengunakan pengaturcaraan logic programming dan LISP. 12. 13. Mapping of Subject to Programme Outcomes : Programme Outcomes Apply soft skills in work and career related activities To make use of fundamentals concepts and formulate best practices. Apply technical concepts and practices in specialized areas of Computer Science Analyze the requirements to address problems or opportunities faced by organizations Recognize and pursue continued life-long learning throughout their career Blend innovative mind and entrepreneurial skills Relate moral values and professional ethics to the practice of an ICT professional. Assessment Methods and Types : Description/Details Method and Type Coursework: Midterm test Quizzes and Assignment % of Contribution 5 30 20 30 5 5 5 Percentage 30% 30% Final Exams 40% 14. Details of Subject Topics Introduction History and definition of Artificial Intelligence; AI problems and problem spaces: Game Playing; Planning; Understanding; Natural Language Processing; Parallel and Distributed AI; Learning; Connectionist Model; Common Sense; Expert Systems; Perception and Action; Fuzzy Logic; Neural Network. Intelligent Agents Agent and Environments; Good Behaviour: Concept of Rationality; The Nature of Environments, The structure of agents Problem Solving Solving Problems by Searching; Problem-Solving Agents; Example Problems; Searching for Solutions; Uninformed Search Strategies; Searching with Partial Information; Informed Search and Exploration; Informed (Heuristic) Search Strategies; Heuristic Functions; Local Search Algorithms and Optimization Problems; Game Playing; Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) and backtracking search for CSPs. Knowledge and Reasoning I Knowledge Representation: Logical Agents; Agents based on Propositional logic; The meaning of knowledge; Semantic Nets; Difficulties with Semantic Nets; Object-Attribute-Value Triples; Frames; Difficulties with Frames; Logical Agents; Knowledge and Reasoning II First- Order Logic; Inference in First-Order Logic; Propositional vs. First-Order Inference; Inference rules for quantifiers; Reduction to propositional inference; A first-order inference rule; Unification; Firstorder definite clauses; Resolution; Conjunctive normal form for firstorder logic; The resolution inference rule; Example proofs; Completeness of resolution; Resolution strategies Acting Locally Planning; A Simple planning agent; From problem solving to planning; Planning in Situation Calculus; Basic representations for planning; A partial-order planning example; A partial-order planning algorithm; Planning with partially instantiated operators. Learning Forms of Learning; Inductive Learning; Learning Decision Trees; Decision trees as performance elements; Expressiveness of decision trees; Inducing decision trees from examples; Choosing attribute tests; Assessing the performance of the learning algorithm; Noise and over-fitting; Broadening the applicability of decision trees; Ensemble Learning and Computational Learning Theory. Mode of Delivery Lecture Tutorial/Lab 2 2 2 2 8 8 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 Total 15. 16. 28 28 Lab / Tutorial : Learn LISP Programming for AI Problem Solving Apply different search techniques (e.g. DFS, BFS and Heuristic search) to solve a given problem. Learn about First-Order Predicate Logic, Game playing and/or Machine learning Total Student Face to Face Total Guided and Independent Learning Learning Time (SLT) (Hour) 17. 18. Lectures Tutorials + Quiz Midterm test (1) Assignment (1) 28 28 1 0 28 28 6 10 Quizzes 1 4 Final exam (1) 2 16 SUBTOTAL 60 106 Total SLT Credit Value Reading Materials : Textbook J. Russell and Peter Norvig ; “Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach “, 2nd Edition., 2003. 179/40 = 4 Reference Materials Bratko, I., "Prolog programming for Artificial Intelligence", 3rd Edition, Addison-Wesley, 2000. T. Dean, J. F. Allen & Y. Aloimonos, Thomas Dean, and James Allen, and Yiannis Aloimonos, "Artificial Intelligence: Theory and Practice", Benjamin Cummings, 1995. George F. LUGER; “Artificial Intelligence: Structure and Strategies For Complex Problem Solving; 6th Edition, PEARSON, Addison Wesley2009 19. StrategiesUCTURE AND STRATEGIES FOR Complex Problem Solving Appendix (to be compiled when submitting the complete syllabus for the programme) : 1. Mission and Vision of the University and Faculty 2. Mapping of Programme Objectives to Vision and Mission of Faculty and University 3. Mapping of Programme Outcome to Programme Objectives 4. Progarmme Objective and Outcomes (Measurement and Descriptions)