After completion of this subject, students should be able to
advertisement

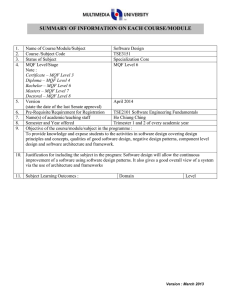
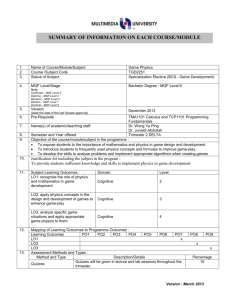
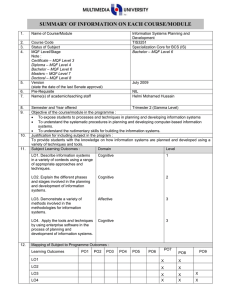
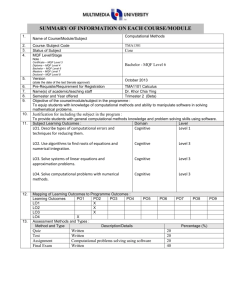
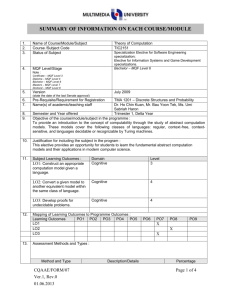
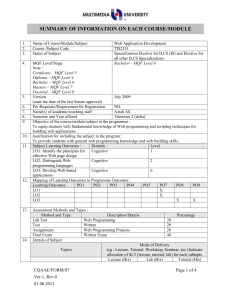
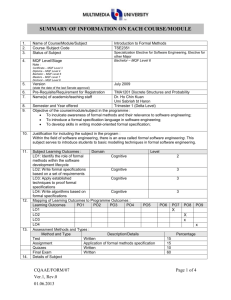
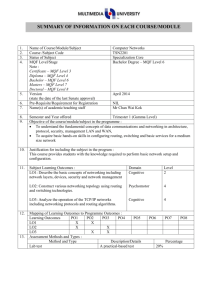
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Name of Course/Module Course Code Status of Subject MQF Level/Stage Note : Certificate – MQF Level 3 Diploma – MQF Level 4 Bachelor – MQF Level 6 Masters – MQF Level 7 Doctoral – MQF Level 8 Version (state the date of the last Senate approval) Software Design TSE3151 Elective Bachelor Degree – MQF Level 6 Pre-Requisite Name(s) of academic/teaching staff TSR2701 Software Requirement Engineering Year 2012 Wan Ruslan Yusoff Semester and Year offered Objective of the course/module in the programme : To provide knowledge and expose students to the activities in software design covering design principles and concepts, qualities of good software design, negative design patterns, component level design and software architecture and framework. Subject Learning Outcomes : After completion of this subject, students should be able to: 11. Discuss the qualities of good software design Evaluate the quality of multiple software design based on key design principles and concepts Identify and avoid negative patterns in the construction of a software application Create and specify the software design for a medium sized software using a software requirement specification, an accepted program design methodology and appropriate notation Evaluate a software design at component level Synopsis: The major areas covered are software design concepts and principles, negative design patterns, component level software design, software design qualities, and software architecture and frameworks. Bidang utama bagi kursus ini meliputi konsep dan prinsip rekabentuk perisian, rekabentuk perisian negatif, rekabentuk perisian paras komponen perisian, kualiti rekabentuk perisian, serta senibina dan bingkai kerja perisian. 12. Mapping of Subject to Programme Outcomes : % of Programme Outcomes Apply soft skills in work and career related activities To make use of fundamentals concepts and formulate best practices. Apply technical concepts and practices in specialized areas of Computer Science Analyze the requirements to address problems or opportunities faced by organizations Recognize and pursue continued life-long learning throughout their career Blend innovative mind and entrepreneurial skills 13. Relate moral values and professional ethics to the practice of an ICT professional. Assessment Methods and Types : Method and Type Description/Details Contribution 5 40 15 20 10 5 5 Percentage Coursework 40% Final Examination 60% Total 100% 14. Details of Subject Topics Mode of Delivery Lecture Tutorial/Lab 2 - 4 4 Negative Design Patterns What are negative design patterns Goals of negative design patterns Benefits of negative design patterns Using negative design patterns Discovering new negative design patterns Analysing negative design patterns 6 6 Components Level Software Design What are software components UML Component Notation Case study of component in use What components consists of Component life cycle Corba Component Standards Software Design Qualities 4 Introduction to Software Design What is software design Building model Transferring design knowledge Constraints of the software design process and product Recording software design decisions Fundamental design concepts and principles Goals of software design Correctness Robustness Flexibility Reusability Efficiency Tradeoff analysis of Robustness, Flexibility, Reusability and Efficiency 4 6 6 6 6 Software Quality concept Assessing software design quality Quality attributes of the design product Assessing the design process Architecture and Frameworks Meaning of software architecture Goals for architecture and modularization Modularization, cohesion and coupling Standard software architecture Meaning of Framework Framework Usage Goals for Framework Framework development and example Total 15. 16. 28 26 Lab / Tutorial: Total Student Learning Time (SLT) Face to Face Total Guided and Independent Learning (Hour) Lectures 28 28 Tutorials 26 26 Midterm test (1) 1 12 Assignment (1) 1 12 Quiz (2) 1 4 Final exam (1) 2 20 Total 59 102 161/40 = 4 Total SLT 17. 18. Credit Value Reading Materials : Textbook David Budgen, Software Design (2nd Edition), Addison Wesley, 2003 Eric J. Braude, Software Design: From Programming to Architecture (First Edition), Wiley, 2003 4 Reference Materials Martin Fowler, Kent Beck, John Brant, William Opdyke, Don Roberts, Refactoring: Improving the design of the existing code, Addison-Wesley Professional, 1999. 19. Bernd Bruegge, Allen H. Dutoit, Object Oriented Software Engineering Using UML, Patterns and Java (Second Edition), Prentice Hall, 2003 Erich Gamma, Richard Helm, Ralph Johnson, John Vlissides, Design Patterns: Elements of Reusable Object-Oriented Software, AddisonWesley, 1995 (Classic and famous seminal book for software design patterns.) Appendix (to be compiled when submitting the complete syllabus for the programme) : 1. Mission and Vision of the University and Faculty 2. Mapping of Programme Objectives to Vision and Mission of Faculty and University 3. Mapping of Programme Outcome to Programme Objectives 4. Progarmme Objective and Outcomes (Measurement and Descriptions)