Study guide for Atmosphere, Weather, and Climate Test (Chap 24)
advertisement

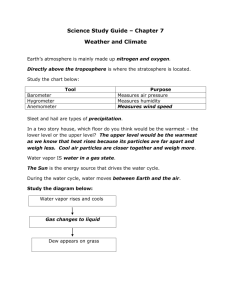
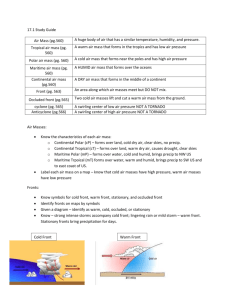
Weather Self-Test/Practice Questions 1. Use this data to answer questions that follow: Relative Humidity Town A 50% Town B 99% Town C 75% Town D 5% (a) Which town is closest to being saturated? __B___ (b) In which town is it probably raining? ___B___ (c) Which town has the driest air? __D___ 2. Use this data to answer questions that follow: Temp (F) Happy, NJ 52 Sad, NV 52 Boredom, ND 52 Dew Point Temp (F) 48 11 40 (a) By how many degrees does the temperature need to drop for dew to form in Happy, NJ?_____4 degrees______ (b) In which city is dew most likely to form? ____Happy, NJ____ (c) Which city must have the lowest relative humidity? ___Sad, NV_____ (d) In which town would frost form if temperature suddenly dropped to the dew point? ____Sad, NV____ 3. Name the cloud: Layered cloud, but raining High altitude, wispy Mid-altitude, layered cloud Mid-altitude, puffy appearance Puffy, fair-weather cloud Tall, thunderstorm producing cloud _____numbostratus_________ _____cirrus_______ _____altostratus_______ _____altocumulous___________ _____cumulous___________ _____cumulonimbus___________ 4. Name the type of precip that most closely matches the description Sleet Freezing Rain Hail Snow __Sleet__(a) Snow melts in a narrow warm air layer aloft, but has time to refreeze before hitting the ground __F.R.__(b) Snow melts in a deep (thick) warm air layer aloft, but does not have time to refreeze while falling. So this type of precip freezes on the ground and on surfaces. ___Hail___(c) This form of frozen precip (> 5mm) forms in cumulonimbus clouds during thunderstorms. __snow__(d) This form of frozen precip falls from clouds when temperatures are below freezing from the clouds all the way to the ground (i.e., no warm layer aloft) 5. Name the air mass type that is described: (a) Air masses that come from the north over land in North Dakota (from the North) are _______cP_______ ___________________. (b) Air masses that come from the south over land in Mexico are _______cT________ ___________________. (c) Air masses that come to NJ from the northeast from over the Atlantic Ocean are __________mP______ ___________________ (d) Air masses that come from the south from over the Gulf of Mexico are_________mT_______ ___________________. 6. Match these descriptions to the type of front (either cold front or warm front) ___cold_____ (a) Warm air rises quickly, forming tall cloud formations. ___ cold _____ (b) Cumulonimbus clouds ___warm_____ (c) Nimbostratus clouds near the front boundary. __ cold ______ (d) Duration of front passage usually a few hours __ warm _____ (e) Duration of front passage usually a few days (increasing clouds then rain) __ warm ______ (f) Temperatures higher after passage of front ___ cold _____ (g) Temperatures drop after it passes ___ cold _____ (h) Thunderstorms possible ___ warm _____ (i) Warm air rises more gently ___ warm _____ (j) Gentle rain (instead of thunderstorms) 7. Front with no net advancement of cold or warm air masses is called a ___________ front. 8. Draw a sketch or describe what is occurring with air masses at an occluded front: cold air (or cold front) catches up to warm front. Warm air trapped between. Happens because of rotation around Mid-Latitude Cyclones. 9. The weather produced at an occluded front is most similar to a [cold; warm; stationary] front. 10. Draw the map symbols for each of the fronts Cold Warm Stationary Occluded note: know these symbols in black and white (note sides that triangle are on) 11. Occluded fronts occur because of circulation of air around ___low___ pressure systems, which are also known as Mid-Latitude Cyclones. 12. Match each of these statements as correlating with either low pressure or high pressure systems. Write the word High or Low on the line. ____Low___ ____High______ ____ High ______ ____ Low ______ ____ High ______ ____ Low ___ ____ High _____ (a) Rainy weather (b) Fair weather (c) Clockwise air rotation in Northern Hemisphere (d) Counterclockwise air rotation in Northern Hemisphere (e) Clockwise air rotation in Southern Hemisphere (f) Air moves inward and rises (g) Air sinks and moves outward 13. Use the map to answer the questions that follow. C B A cP mT (a) The curvy lines on the map are called ____isobars____. (b) Put “cP” on the map in the U.S. at the location of a continental polar air mass. (c) Put “mT” on the map in the U.S. at the location of the maritime tropical. (d) What is the wind direction at location A? __N or NE____ (e) What is the wind direction at location B? ___S or SW___ (f) What is the wind direction at location C? __S or SE____ (g) At location B, temperatures will [increase; decrease] during the next few hours.