Air mass
advertisement
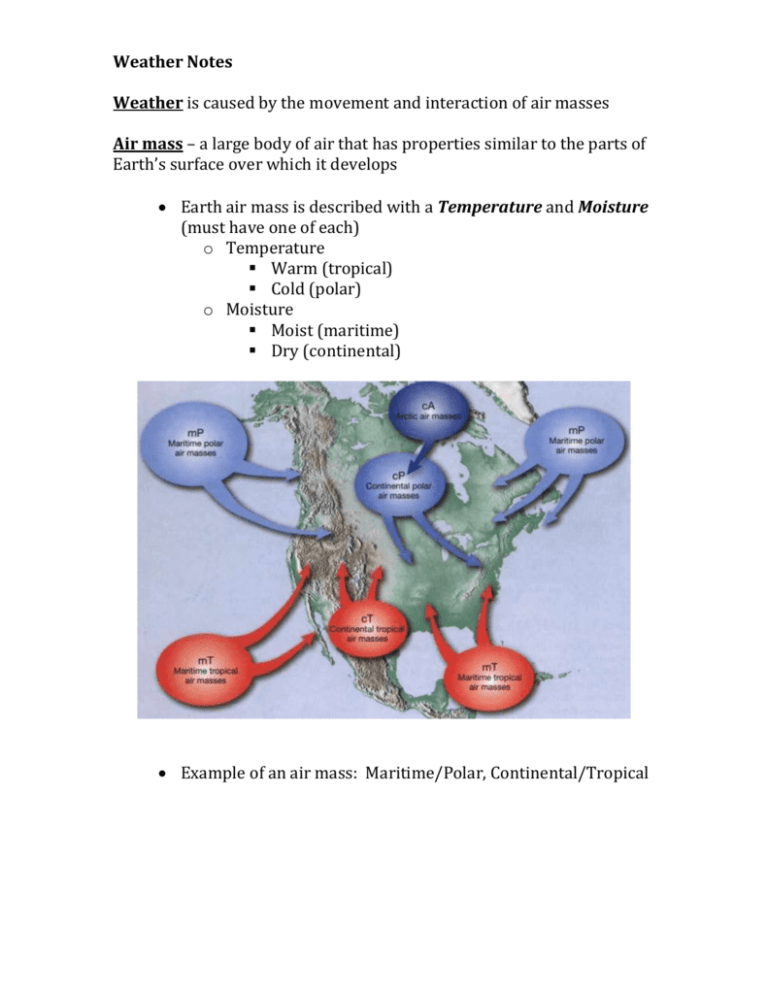
Weather Notes Weather is caused by the movement and interaction of air masses Air mass – a large body of air that has properties similar to the parts of Earth’s surface over which it develops Earth air mass is described with a Temperature and Moisture (must have one of each) o Temperature Warm (tropical) Cold (polar) o Moisture Moist (maritime) Dry (continental) Example of an air mass: Maritime/Polar, Continental/Tropical Pressure Systems High pressure system: o High pressure does not allow air to rise and form clouds o Gives Fair/nice, “good” weather o Moves clockwise (in northern hemisphere) o HINTS: giving a “HIGH 5” = GOOD “thumbs up/high” = GOOD HIGH (4 letters), GOOD (4 letters) Low pressure system o Low pressure allows warm air to rise, which forms clouds o Gives cloudy, “bad” weather, usually with precipitation o Moves counter-clockwise (in northern hemisphere) o HINTS: “thumbs down” = bad LOW (3 letters) = BAD (3 letters) Fronts - a boundary that forms between 2 different air masses Usually cloudy and stormy at a front boundary 4 types of fronts o Cold Front, Warm Front, Stationary Front, Occluded Front Front Description of Front Cold Front - - cold air rapidly pushes up warm air can result in rain, large thunderstorms, and possible tornadoes (“drama queens”) leaves a colder air mass over area, temps may drop Warm Front - - warm air moves over a receding (leaving) colder air mass results in several hours, or days of precipitation Weather Map Symbol Front Description of Front Stationary Front - - warm air and cold air meet little or no movement between air masses results in light precipitation and wind for several days Occluded Front - - involves 3 air masses of different temperatures 2 air masses “squeeze” and force warmest air mass upward causes precipitation Weather Map Symbol Severe Storms Thunderstorms/Hail o Usually occurs along cold fronts o Heavy rain, lighting, thunder, heavy winds o Hail may form Hail – ice crystals that form and grow larger through updrafts and down drafts in thunder clouds Tornadoes o Violently rotating columns of air that make contact with the ground o Formed during severe thunderstorms o Strong winds move in many directions at many speeds causing a rotating column parallel with the ground. The updraft of the thunderstorm causes the column to tilt vertically (up and down). When the column hits the ground, it is called a tornado. o Tornado alley – a group of states in the midwest prone to tornadoes due to the severity of thunderstorms and flat land Hurricanes o most powerful severe storm o large, swirling, low pressure system that forms over warm water o turns heat energy from the ocean into wind Blizzards o Severe snow storms o Strong winds with low visibility due to falling snow o Low temperatures o Must continue for at least three hours Severe Weather Safety o National Weather Service will announce watches and warnings through various tools (i.e. radio, computer websites, twitter, facebook, text messaging, television) o Seek shelter indoors when possible o Secure loose items outside o Evacuate if requested by government/National Weather Service











