Assessment and management of thoracic injuries
advertisement

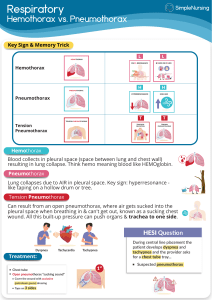
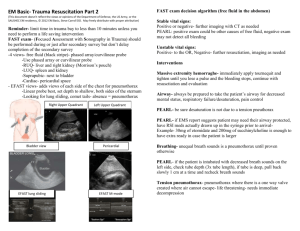
Assessment and management of thoracic injuries Aim: The trainee should have an understanding of common injuries to the chest of a child including the work-up and initial management of such patients. Objectives: Knowledge objectives: The trainee should have acquired the following knowledge: An understanding of the anatomy of the chest wall and intrathoracic viscera An understanding of the pliability of the chest wall in younger children, such that internal injuries may occur without evidence of injury to the thoracic cage. An understanding of the increased predisposition of children to hypoxia due to: o Airway is more prone to obstruction o Low functional residual capacity o Predominant use of diaphragm for breathing o Susceptibility to pulmonary contusion. o Relative ease of displacement of an endotracheal tube due to short length of the trachea o Relatively high mobility of the mediastinum, with a subsequent higher predisposition of rapidly developing tension An understanding of the relative risks of certain injury patterns relative to adults: o Increased risk of pulmonary contusion o Increased risk of tension with a pneumo- or hemothorax o Lower risk of great vessel and esophageal injury An understanding of the mechanism, pathophysiology and clinical presentation of traumatic asphyxia An understanding of the radiologic findings and management of pulmonary contusion An understanding of the clinical findings during the primary survey of a: o tension pneumothorax o simple pneumothorax o open pneumothorax o Flail chest o Massive hemothorax o Cardiac tamponade o Airway obstruction Know the management principles for the treatment of life-threatening injuries during the primary survey, including o Needle decompression o Chest tube thoracostomy o Intubation o Pericardiocentesis An understanding of the clinical and radiologic findings of a: o simple pneumothorax o Hemothorax o Pulmonary contusion o Tracheobronchial disruption o Blunt cardiac injury o Traumatic diaphragmatic injury o Possible aortic injury Differentiation of the pathophysiology between a simple, open and tension pneumothorax Initial management of a patient with a simple, tension or open pneumothorax Management of a massive hemothorax Know how to identify clinically significant blunt cardiac injury using ECG or appreciate the role of echocardiography in making the diagnosis. Initial management of a patient suspected of having a cardiac tamponade Mechanisms of injury and clinical and radiologic indices that raise suspicion for an aortic injury Management of penetrating injuries in general Demonstrate a knowledge of the radiographic assessment for blunt aortic injuries. Indications for emergency thoracotomy (not in the ED) o Penetrating wound of the heart or great vessels o Massive or continuous intrathoracic bleeding o Open pneumothorax with major chest wall defect o Evidence of injury to aorta or major vascular branch thereof o Massive on -going airleak indicating injury to a major airway o Cardiac tamponade o Esophageal perforation o Diaphragmatic rupture o Penetrating chest trauma with persistent hypotension despite maximal resuscitation Indications for Emergency Department thoracotomy o For post-traumatic witnessed arrest or near arrest if: Penetrating thoracic trauma Blunt trauma with acute deterioration but signs of life initially in the ED Skills objectives: The trainee should have an understanding of the following skill set: A systematic way to review a supine AP chest xray An ability to identify on CXR major thoracic injury radiologic features: o Rib/clavicular fractures o Pneumothorax – simple and tension o Hemothorax o Pulmonary contusion o Widened mediastinum Performance of a needle thoracentesis for a presumed tension pneumothorax Insertion of a chest tube by an open technique or closed seldinger-type technique Know how to connect the tube thoracostomy system to suction Performance of a pericardiocentesis in the case of suspected cardiac tamponade Have an understanding of how to perform an ED thoracotomy