Pneumothorax
advertisement

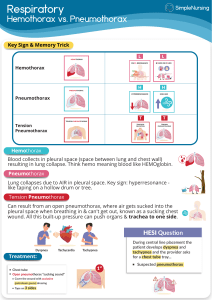
Pneumothorax Pneumothorax Defined Definition – “What?” “Pneumo”- gas “Thorax” – chest cavity Analagous to Pleural Effusion Pathophysiology – “How? Pleural space Baseline (-) pressure space Parietal Pleura Visceral Pleura Normal inspiration Diaphragm Transmit (-) Pressure Pathologic inspiration XS gas disrupts transmission of () pressure Types of Pneumothorax Spontaneous Pneumothorax Primary - rupture of subpleural bleb “Jimmy is a tall, wiry, 21-year old male, who plays trombone in the marching band….” Secondary - underlying lung/pleural disease – emphysema Chronic bronchitis, asthma, TB, … #1 Traumatic Pneumothorax Open Chest wall is penetrated : outside air enters pleural space Closed Chest wall is intact Ex. Fractured rib Types of Pneumothorax 2 Tension Pneumothorax “Ball-valve mechanism” Injury to pleura creates a tissue flap that opens on inspiration and closes on expiration One of our own patients Variations Hemo-thorax Chylo-thorax Injury to thoracic duct Empyema Parapneumonic effusions in communityacquired pneumonia Symptoms Dyspnea Pleuritic chest pain Nerve endings at pleural capsule Sense of impending doom Sudden onset Tension pneumothorax Spontaneous pneumothorax Physical Exam - Signs Unstable patients vs. Stable patients Vital Signs Asymmetric chest expansion Deviated trachea Diminished breath sounds unilaterally Hyper-resonance unilaterally Decreased tactile fremitus Diagnosis Unstable patient Thoracentesis Rapid release of air Vital signs stabilize rapidly Stable patient CXR Monitor size by measuring distance from lateral lung margin to chest wall Be sure that pneumothorax is not expanding Imaging Plain Radiographs Upright PA on inspiration Detect other pathologies: pneumonia, cardiac, etc. Partially collapsed lung Tension Pneumothorax Trachea and mediastinum deviate contralaterally Ipsilateral depressed hemidiaphragm Chest CT Not routine Only to assess the need for surgery (thoracotomy) Treatment Small pneumothorax Resolve over days to weeks Supplemental oxygen and observation Tension pneumothorax Immediate decompression via chest tube or needle thoracostomy Spontaneous pneumothorax – outpatient, f/u with serial CXR Symptomatic – inpatient, chest tube Recurrent pneumothorax – CT to evaluate need for thoracotomy Asymptomatic Tube Thoracostomy a.k.a. Chest tube