Social Studies Study Guide
advertisement

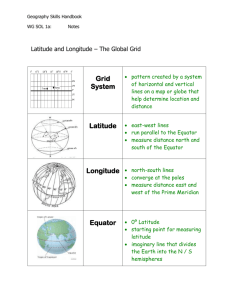
Social Studies Study Guide- Grade 7 Chapters 1 & 2 Test- Monday, October 9th Terms: 1. Latitude: Distance north or south of the Equator, measured in degrees 2. Longitude: Distance east or west of the Prime Meridian, measured in degrees 3. Prime Meridian: The line of the global grid running from the North Pole to the South Pole through Greenwich, England; starting point for measuring degrees of east and west longitude 4. International Date Line: the 180 degree meridian on the opposite side of the Earth (opposite the Prime Meridian) 5. Equator: Imaginary line that runs around the earth halfway between the North and South Poles; used as the starting point to measure degrees of north and south latitude 6. Tropic of Capricorn: When the sun’s direct rays strike the line of latitude (23 ½ degrees South Latitude) 7. Tropic of Cancer: When the sun appears directly overhead at the line of latitude(23 ½ degrees North latitude) 8. North Pole: 90 degrees North latitude 9. South Pole: 90 degrees South latitude 10. Absolute location: The exact location of a place on the earth described by global coordinates 11. Relative location: Describing a place in relation to another place 12. Global Positioning System (GPS): A special device that receives signals from satellites 1 13. Map Types i. Physical: This type of map shows landforms and water features ii. Political: This type of map shows the names and boundaries of countries, the location of cities and other human-made features of a place. iii. Special purpose: This type of map shows specific topics in details (could show rainfall, population) iv. Contour: This type of map is a physical map that shows elevation 14. Landform: Individual features of the land such as mountains and valleys 15. Region: An area that shares common characteristics 16. Fossils: are the remains of animals, plants, and other organisms from the past 17. Orbit: A path that the planets travel along 18. Summer solstice: The day with the most hours of sunlight and the fewest hours of darkness; also known as the beginning of summer 19. Winter solstice: This is the day with the fewest hours of sunlight; it marks the first day of summery in the southern hemisphere 20. Vernal equinox: When there is 12 hours of daylight and 12 hours of night; it’s the start of spring 21. Autumnal equinox: The day the sun is directly over the equator as it head south 22. Core: The center of the earth that is made up of magma 23. Mantle: A layer of rock which surrounds the core 24. Magma: Melted rock that flows to the surface during a volcanic eruption 25. Crust: The uppermost layer of the earth 26. Plates: Huge slab of rock that makes up the Earth’s crust 2 27. Earthquake: A violent and sudden movement of the earth’s crust 28. Glaciers: Giant, slow moving sheets of ice 29. El Nino: A combination of temperature, wind, and water effects in the Pacific Ocean 30. La Nina: This is the opposite of El Nino; winds from the east become very strong, cooling more of the Pacific- heavy clouds form in the western Pacific 31. Atmosphere: Layer of air surrounding the earth 32. Lithosphere: the Earth’s crust 33. Hydrosphere: refers to the Earth’s surface water and groundwater 34. Biosphere: the collection of plants and animals of all types that live on Earth 35. Rain shadow: when mountains have an effect on rainfall that blocks rain from reaching interior regions 36. Deforestation: cutting down forests without replanting Things to Know: The different seasons of Earth are caused by the Earth’s tilt at 23.5 degrees. The water cycle is a process in which water circulates from the land to the sky and back down again. Parts of the water cycle: precipitation, collection, evaporation, condensation. 3 The earth is constantly changing for many reasons, one being plate tectonics where plates have been moving and pushing against each other very slowly for millions of years. Sometimes the plates slip or move and cause an earthquake. We have leap year because the Earth revolves around the sun 365 ¼ days and every four years, we account for the ¼ day (February 29th). 5 Climate Zones 1. Tropical: the area along the equator between the Tropic of Cancer (23.5 degrees N. lat) and the Tropic of Capricorn (23.5 degrees S. lat) a. Hot and humid, abundant rainfall, good amount of sun 2. Mid-Latitude: found in Northern and Southern Hemispheres between the Tropic of Cancer and 60 degrees N. lat and between the Tropic of Capricorn and 60 degrees S. lat a. Most of the world’s population live here, four seasons 3. High Latitude: regions that lie in the high latitudes of each hemisphere (60 degrees North Pole and 60 degrees South Pole) a. Temperature = cold 4. Dry: receives little or no rain, hot during the day and cold at night, found in any latitude (Great Plains in America) 5. Ice Cap/Arctic: found on the polar regions, average temperature is below 0, vegetation lichens and mosses live on rocks Benefits from Tropical Rainforest: medicine, toys, food, chocolate, shelter, furniture (wood), clothing material, helps maintain the temperature in other parts of the world Chemicals in air pollution can combine with precipitation which then falls as acid rain. Acid rain kills fish and eats away at the surfaces of buildings and can destroy an entire forest. The difference between weather and climate is that weather can change day by day (precipitation, wind, temperature, etc) but climate is the average wind, temperature, and precipitation over a large period of time. 4 You can find saltwater in the 4 major oceans. You can find freshwater in lakes and rivers. Tropical Rainforest (the world’s largest tropical rainforest area is found in The Amazon Basin) - rains all year long - full vegetation - thick forest - has canopy layer (tops of trees that form a ceiling) - home to millions of animals and plants Tropical Savanna - grasslands with scattered trees - subtropical and tropical latitudes. - The dry season is marked by months of drought and fire which are essential to the maintenance of savannas. Greenhouse Effect: the buildup of certain gases in the atmosphere that hold more of the sun’s warmth The 7 Continents 1. Africa 2. Antarctica 3. Asia 4. Australia 5. North America 6. South America 7. Europe The 4 Oceans 1. Atlantic 2. Pacific 3. Indian 4. Arctic 5 Map Projections: Ways of showing the earth on a flat surface Goode - very little distortion - similar to a peeled grapefruit - continents are close to their true shapes and sizes Robinson latitude lines are parallel, but longitude lines are NOT parallel minor distortions but most distorted at North and South Poles Mercator - latitude lines are parallel, longitude lines are parallel - shows landscapes accurately but not size or distance - greater distortion the farther from the equator Winkel Tripel neither latitude nor longitude lines are parallel land areas are LESS distorted than other projections good overall view of the continents’ shapes and sizes 6