Tissues:
advertisement

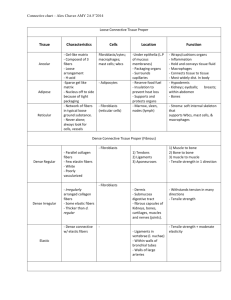
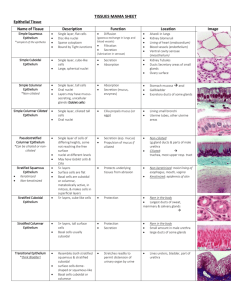
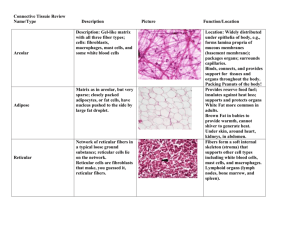
Tissues: Four classes Epithelium Connective Muscle Nervous Tissues are: group of similar or identical cells that share a common function. used to build organs Overview: Epithelial o Line body cavities o Cover free surfaces o Including ducts and glands o Tightly connected to each other o Exposed to a space on their free surface o Tightly connected to deeper tissue with a glue-like membrane called the basement membrane o **best function is absorption, secretion and protection Muscle o Provide movement for the body o Contain fibers made up of myosin and actin protein filaments Nervous o Conduct electrical impulses o Composed of one cell type … the neuron o Neurons have Nucleus Several dendrites One or several axons o Normal pathway follows: Dendrite to Cell body to Axon Produces a substance called a neurotransmitter Allows impulse to jump o Neuron to neuron o Neuron to muscle o Neuron to gland o classified by function and structure function sensory motor association structure unipolar bipolar multipolar What you see microscopically is specific neurons (rather than tissues as in the other three classes) Epithelial Tissue: has a free edge packed end to end avascular has nerve supply Specific Location Simple Squamous Lungs – alveoli Capillaries, ear cochlea, heart lining, serous membranes Kidney tubules, glands, ducts and anterior lens of the eye GI Tract from stomach to anus, ducts, glands and gall bladder Skin, mouth, vagina, esophagus, and eye Simple Cuboidal Simple Columnar Stratified Squamous Function (at that site) Rapid exchange: Diffusion, osmosis and filtration Rapid exchange: Secretion and absorption Secrete and absorb Protect Stratified Cuboidal Ducts of adult sweat glands, male urethra Protection Stratified Columnar Submandibular salivery gland and male urethra. Anal mucous membrane Protect and secrete Transitional Baler, ureters, urethra Distention Ciliated Columnar Upper respiratory tract, fallopian Moves fluids or particles along a General Comments Fried egg – scale like, saran wrap thin, joined end to end, low wear and tear Round nuclei Secretion of mucus, sweat, etc. Oval nuclei, contain microvilli (small hairs) and goblet cells. + surf. Area Several layer, great wear, deep cell. Can be cuboidal/columnar. Keratinzed = skin, nonkeratinized = mouth, esophagus, vagina, tongue Cicular nucleus Columnar only in superficial layer. Deep layers all different shapes = polyhedral Squamous to cuboidal in shape, able to stretch Have goblet cells, have cilia, make tubes, central canal of spinal cord pathway via cilliary action ovum move down fallopian tube Connective Tissues Specific Location Function General Comments Areolar Subcutaneous layer of skin around organs Subcutaneous layer of skin, kidneys, joints and eyes Framework of liver, spleen and lymph nodes Tendons and ligaments Strength, elasticity, support Collagen, elastic, reticular, fibroblast, macrophage, plasma Adipocytes, store triglycerides Lung tissue, walls of arteries, trachea and bronchial tubes Ends of long bones, rib ends, nose, larynx, trachea Allows stretching Support Bluish with shiny collagen fibers with chondrocytes Pubic symphasis, vertebral discs and knee menisci Epiglottis, external ear, Eustachian tubes Everywhere Support Chondrocytes among collagen Support and shape Chondrocytes and elastic fibers Support, protect, store and hematapoesis Transport gasses, phagocytosis and allergic rxn Haversion system, lamellae, lacunae, osteocytes Plasma, platelets and WBC’s Adipose Dense Regular Collagenous Dense Regular Elastic Dense Irregular Elastic Hyaline Cartilage (most abundant type of cartilage) Fibrocartilage Elastic Cartilage Bone Blood Within blood vessels Reduce heat loss, emergency reserve, support, protect Strong attachments between structures Mostly collagen fibers, fibroblasts between bundles Elastic fibers, fibroblasts MUSCLE SPECIFIC LOCATION FUNCTION GENERAL COMMENTS Striated, light and dark bands. Many nuclei in fiber(s) SKELETAL Attached to bone Motion, posture, heat CARDIAC Walls of heart Pump blood to all parts of body Striated, involuntary, usually only one fiber per nuclei SMOOTH Constrict blood vessels, break down food, move foods and fluids Found in walls of vessels, airway stomach, intestine, gall bladder and urinary bladder Involuntary, nonstriated, one nucleus NERVOUS Neurons: Sensory Motor Unipolar Bipolar Multipolar Parts of the neuron include Nerve: NERVOUS Neurons: Have the ability to respond to stimuli and convert tem into nerve impulse(s). A nerve impulse is a tiny electrical/chemical current. Sensory (afferent) toward brain or cord Motor (efferent) away from brain or cord Unipolar Bipolar Multipolar Parts of the neuron include the axon, dendrite and cell body. These are labeled A, D and C above. Nerve: bundle of many nerve fibers in the nervous system