Connective Tissue - My Anatomy Mentor
advertisement
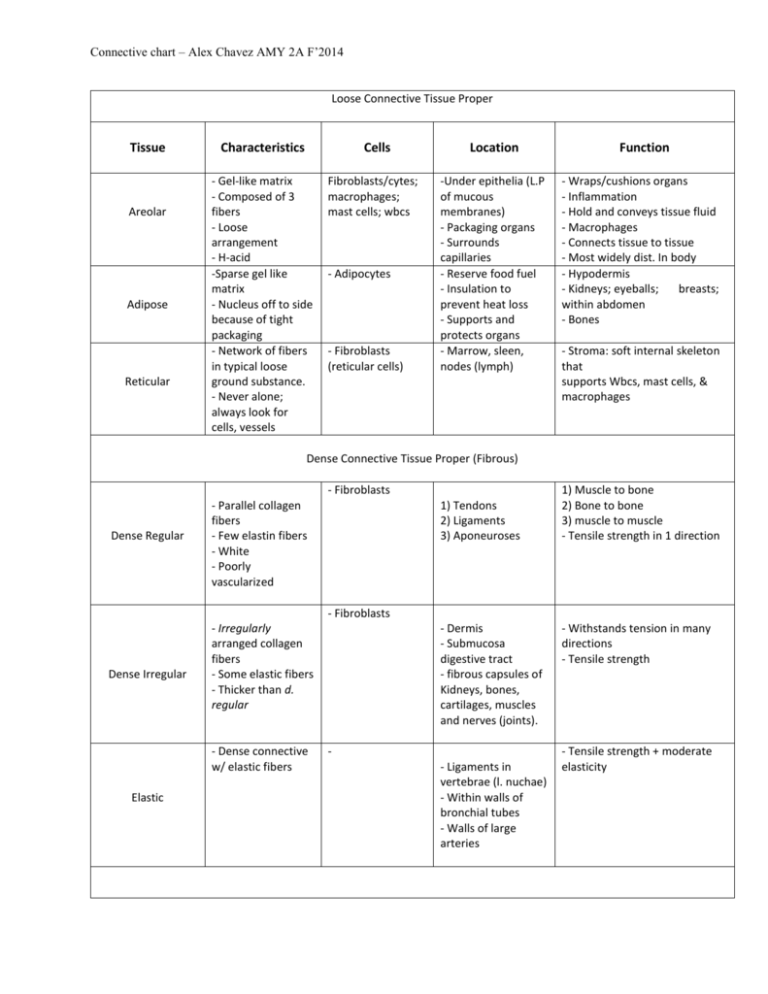
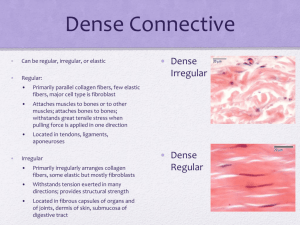
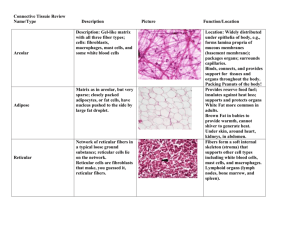
Connective chart – Alex Chavez AMY 2A F’2014 Loose Connective Tissue Proper Tissue Areolar Adipose Reticular Characteristics Cells - Gel-like matrix - Composed of 3 fibers - Loose arrangement - H-acid -Sparse gel like matrix - Nucleus off to side because of tight packaging - Network of fibers in typical loose ground substance. - Never alone; always look for cells, vessels Fibroblasts/cytes; macrophages; mast cells; wbcs - Adipocytes - Fibroblasts (reticular cells) Location -Under epithelia (L.P of mucous membranes) - Packaging organs - Surrounds capillaries - Reserve food fuel - Insulation to prevent heat loss - Supports and protects organs - Marrow, sleen, nodes (lymph) Function - Wraps/cushions organs - Inflammation - Hold and conveys tissue fluid - Macrophages - Connects tissue to tissue - Most widely dist. In body - Hypodermis - Kidneys; eyeballs; breasts; within abdomen - Bones - Stroma: soft internal skeleton that supports Wbcs, mast cells, & macrophages Dense Connective Tissue Proper (Fibrous) - Fibroblasts Dense Regular - Parallel collagen fibers - Few elastin fibers - White - Poorly vascularized 1) Tendons 2) Ligaments 3) Aponeuroses 1) Muscle to bone 2) Bone to bone 3) muscle to muscle - Tensile strength in 1 direction - Fibroblasts Dense Irregular - Irregularly arranged collagen fibers - Some elastic fibers - Thicker than d. regular - Dense connective w/ elastic fibers Elastic - Dermis - Submucosa digestive tract - fibrous capsules of Kidneys, bones, cartilages, muscles and nerves (joints). - Ligaments in vertebrae (l. nuchae) - Within walls of bronchial tubes - Walls of large arteries - Withstands tension in many directions - Tensile strength - Tensile strength + moderate elasticity Connective chart – Alex Chavez AMY 2A F’2014 Cartilage: -Lacks nerves; is avascular; obtains nutrients via diffusion from blood vessels; Ground substance : GAGs chondroitin sulfate and hyaluronic acid, firmly bound collagen fibers. Lacunae: cavities that house small groups of chondrocytes Tissue Hyaline Elastic Fibrocartilage Bone (tissue) Blood Characteristics Cells Location Function - Most abundant - Glassy, blue-white - Firm matrix - Collagen fibers - Chondroblasts - Chondrocytes - Embryonic skeleton - Tip of nose - Rib to sternum connection - Resp. passages Epiphyseal plates: regions near ends of long bones. Articular: Provides cushion at covers of long bones. - Resists compressive stress; cushions. - Support and reinforce - Structure + flexbility - More elastic fibers than Hyaline - Less firm than hyaline - Thick collagen fibers - Intermediate to hyaline and Dense regular (rows of chondrocytes alt. w/rows of thick collagen fibers) - Hard, calcified matrix - Many collagen fibers - Inorganic calcium - Highly vascular - Chondroblasts - Chondrocytes - Chondroblasts - Chondrocytes - External ear (pinna) - Epiglottis - Intervertebral discs - Pubic symphysis - Knee joint - Osteocytes (lacunae) - Osteoblasts - - Bones - Enclosure provides support and protection - Levers for muscles - Storage: calcium, fat, minerals - Hematopoiesis: rbc production - Most atypical - Does not provide support or connection - Blood cells and plasma - Erythroctyes - White blood cells - Platelets - Within blood vessels - Transport vehicle for cardiovascular system - Nutrients, wastes, respiratory gases - Tensile strength + ability to absorb compressive shock